In this article, we will explore the distinction between compost and topsoil. You will learn about their characteristics, uses, and the benefits they provide for off-grid living and gardening. By understanding the differences between compost and topsoil, you will be able to make informed decisions when it comes to soil management and improving the fertility of your garden. So, let’s dive into the topic and discover the unique qualities of compost and topsoil.
Understanding the Distinction: Compost vs Topsoil

Introduction to Compost and Topsoil
When it comes to gardening and landscaping, two key components that play a crucial role are compost and topsoil. While they may seem similar in nature, there are important distinctions between the two. Compost and topsoil have different compositions, nutrient contents, and uses in gardening. Understanding these differences is essential for ensuring healthy plant growth and a thriving garden. In this article, we will explore the characteristics and benefits of compost and topsoil, providing you with the knowledge to make informed decisions for your gardening needs.
Exploring Compost
Compost is a nutrient-rich organic material that is created through the natural decomposition of organic matter such as food scraps, leaves, grass clippings, and plant materials. This process, known as composting, involves the breakdown of these organic materials by microorganisms, resulting in a dark, crumbly substance that is often referred to as “black gold” for gardeners. Compost is typically used to improve soil structure, increase nutrient content, enhance water retention, and promote overall soil health.
Benefits of Compost
The use of compost in gardening offers numerous benefits. It provides a steady release of nutrients, making it an excellent natural fertilizer for plants. Compost also improves soil fertility, enhances soil structure, and aids in moisture retention. Additionally, compost helps to suppress plant diseases and pests, while promoting beneficial microbial activity in the soil. By adding compost to your garden, you are enriching the soil and creating a healthier environment for your plants to grow.
Types of Compost
There are various types of compost available, each with its own unique composition and benefits. Some common types of compost include:
- Manure Compost: This type of compost is made from animal manure and bedding materials. It is rich in nutrients, especially nitrogen, and is ideal for vegetable gardens and flower beds.
- Leaf Compost: Leaf compost is derived from decomposed leaves. It is high in organic matter and provides a good source of nutrients for plants. Leaf compost is often used as a mulch or added to soil to improve its quality.
- Kitchen Compost: Kitchen compost is made from food scraps such as fruit peels, vegetable trimmings, and coffee grounds. It is a convenient way to recycle kitchen waste and create nutrient-rich compost for your garden.
- Mushroom Compost: Mushroom compost is a byproduct of mushroom farming. It is rich in organic matter and nutrients, making it beneficial for promoting plant growth and improving soil quality.

Understanding Topsoil
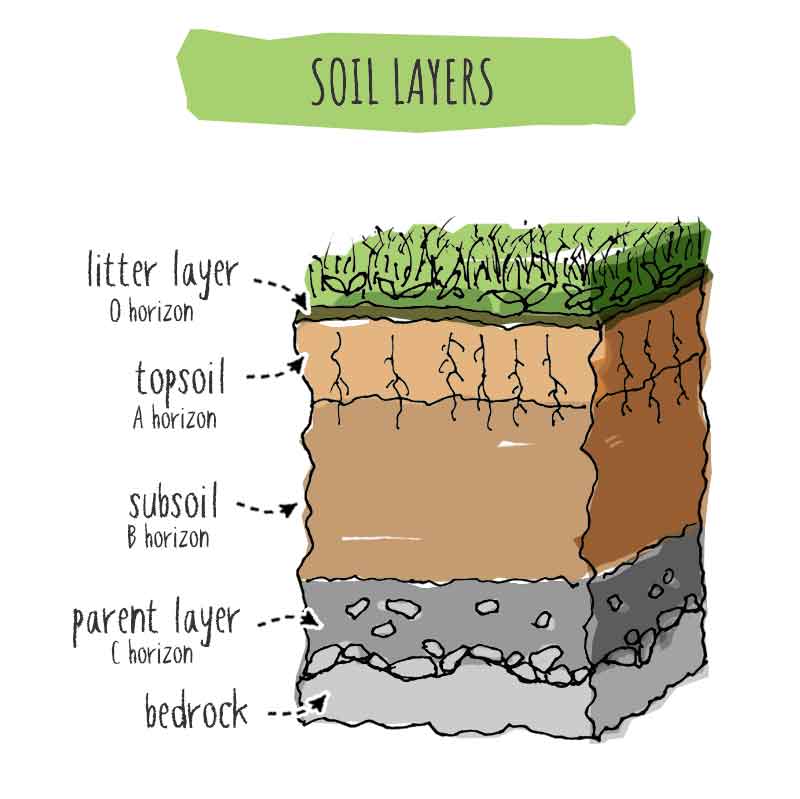
Topsoil, on the other hand, refers to the uppermost layer of soil, which is typically a few inches thick. It is the layer where most of the plant’s root system develops and where the majority of soil nutrients are found. Topsoil plays a vital role in providing plants with the necessary nutrients, water, and support for healthy growth. It is essential for establishing a strong foundation for your garden.
Components of Topsoil
Topsoil is comprised of a mixture of mineral particles, organic matter, water, and air. The mineral particles are derived from the weathering of rocks and minerals, while the organic matter is formed from decaying plant and animal materials. Together, these components create a fertile medium for plant growth. The ratio of mineral particles to organic matter can vary depending on the location and soil composition.

Properties of Topsoil
Topsoil possesses several important properties that influence plant growth. These properties include soil texture, structure, pH level, and nutrient content. Soil texture refers to the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay in the topsoil. Soil structure refers to the arrangement of soil particles, which can affect water infiltration and root penetration. The pH level of topsoil determines its acidity or alkalinity, affecting nutrient availability to plants.
Different Types of Topsoil
Just like compost, there are different types of topsoil based on their composition. Each type varies in terms of nutrient content, water retention, and suitability for specific plants. Some common types of topsoil include:
- Sandy Topsoil: Sandy topsoil has larger particles and drains water quickly. It is well-suited for plants that prefer dry conditions but may require supplemental watering and fertilization due to its lower nutrient content.
- Clayey Topsoil: Clayey topsoil has smaller particles, making it heavy and prone to poor drainage. It can be challenging to work with but retains water well. This type of topsoil requires amendments to improve its structure and prevent waterlogging.
- Loamy Topsoil: Loamy topsoil is a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay. It has excellent water drainage and retention capabilities and provides a fertile environment for plant roots. Loamy topsoil is often considered the ideal type for gardening.
Compost vs Topsoil: Composition
One key distinction between compost and topsoil lies in their composition. Compost is predominantly organic matter, while topsoil is a mix of organic matter and mineral particles. While both are essential for healthy plant growth, compost provides a higher concentration of organic matter and nutrients compared to topsoil.
Compost vs Topsoil: Nutrient Content
Compost is renowned for its nutrient-rich properties. During the composting process, organic materials break down, releasing essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients are in a form that is readily available to plants. In contrast, topsoil contains a lower concentration of nutrients, depending on its composition. It may require amendments or the addition of fertilizer to provide plants with adequate nutrition.

Compost vs Topsoil: Use in Gardening
Compost and topsoil have different uses in gardening. Compost is primarily used as an amendment to improve soil fertility and structure. It is often mixed into existing soil or applied as a top dressing to replenish nutrients. Compost also serves as an excellent medium for starting seedlings and can be used as a mulch to suppress weed growth and retain moisture.
On the other hand, topsoil is used as a foundational layer for planting and establishing gardens. It provides plants with a base for root development and nutrient uptake. Topsoil is typically spread evenly across the planting area or used to fill raised beds and containers.
Compost vs Topsoil: Water Retention
Water retention is another area where compost and topsoil differ. Compost has excellent water-holding capacity, helping to retain moisture in the soil. This property is beneficial in dry climates or for plants that require consistent moisture. Topsoil, depending on its composition, can vary in its water retention capabilities. Sandy topsoil tends to drain quickly, while clayey topsoil holds water for longer periods. The specific type of topsoil chosen will depend on the water needs of the plants being grown.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Compost
When selecting compost for your garden, there are several factors to consider. Firstly, consider the source of the compost. The quality of compost can vary depending on the materials used and the composting process. Look for compost that has been properly decomposed and is free from contaminants. You might also want to consider the nutrient content of the compost, as different plants have varying nutrient requirements. Lastly, consider the purpose of the compost, whether it is for general soil improvement or specific applications like vegetable gardening or flower beds.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Topsoil
Similarly, certain factors should be taken into account when selecting topsoil. Consider the texture and structure of the topsoil, as well as its pH level. Assess its drainage capabilities and whether it requires amendments to improve its quality. Depending on your specific gardening needs, you may also want to consider the nutrient content of the topsoil and its overall suitability for the plants you wish to grow.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while compost and topsoil may have some overlapping properties, they are distinct in composition, nutrient content, and uses in gardening. Compost, with its rich organic matter and nutrient concentration, contributes to soil fertility, improves structure, and enhances water retention. On the other hand, topsoil serves as a foundational layer for plants, providing the necessary support and nutrients for healthy growth. Understanding the distinctions between compost and topsoil is essential for creating a thriving garden and ensuring the success of your plants. By considering the factors mentioned when choosing compost and topsoil, you can make informed decisions and achieve optimal results in your gardening endeavors.




