In this article, we will discuss the topic of how much compost is needed to fill a raised bed. We’ll explore this in the context of off-grid living and gardening. By the end of the article, you’ll have a better understanding of how many bags of compost you’ll need to fill your raised bed. So, let’s get started and find out just how much compost you’ll need for your gardening project.
How much compost is needed to fill a raised bed?
Introduction
Gardening is a rewarding hobby that allows you to reconnect with nature and grow your own food. One popular method of gardening is using raised beds, which offer a range of benefits such as improved drainage and easier access. When it comes to filling a raised bed, one important consideration is how much compost is needed. In this article, we will explore the factors that affect compost requirements and provide tips for successful compost application in a raised bed.
What is compost?
Definition of compost
Compost is a natural soil amendment that is created by decomposing organic materials such as food scraps, leaves, and grass clippings. Over time, these materials break down into a nutrient-rich substance that can be added to garden beds to improve the fertility and structure of the soil.
Benefits of using compost
Using compost in garden beds offers a variety of benefits. Firstly, it enriches the soil with essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are vital for healthy plant growth. Additionally, compost improves the soil’s ability to retain moisture, reducing the need for frequent watering. It also enhances soil structure, making it easier for plant roots to penetrate and access nutrients.
What is a raised bed?
Definition of a raised bed
A raised bed is a gardening technique that involves creating a contained growing space elevated above ground level. This can be achieved by constructing a wooden or stone frame and filling it with soil. Raised beds offer several advantages over traditional in-ground gardening, including better control over soil quality, improved drainage, and reduced weed growth.
Advantages of using raised beds
Raised beds provide several benefits that make them a popular choice among gardeners. Firstly, they offer better drainage, preventing waterlogging and ensuring that plant roots do not become waterlogged. This is particularly useful in areas with heavy clay soils. Raised beds also warm up more quickly in the spring, allowing for earlier planting and extending the growing season. Additionally, the raised height of the bed makes gardening more accessible, especially for individuals with physical limitations.
Importance of compost in a raised bed
Nutrient-rich soil
One of the primary reasons why compost is essential in raised beds is its ability to enrich the soil with essential nutrients. When organic matter decomposes, it releases a range of macro and micronutrients that are vital for plant growth and development. By incorporating compost into a raised bed, you are ensuring that your plants have access to a steady supply of nutrients throughout the growing season.
Improved drainage and water retention
Another important benefit of compost in raised beds is its effect on drainage and water retention. Compost improves the soil’s structure, making it more porous and allowing for better drainage. This is particularly useful in raised beds, where excess moisture can lead to waterlogged roots and plant stress. At the same time, compost also improves the soil’s water-holding capacity, helping to retain moisture during dry periods and reducing the frequency of watering.

Calculating the volume of a raised bed
Measuring the dimensions of the bed
Before determining how much compost is needed to fill a raised bed, you must first measure its dimensions. Using a tape measure, measure the length, width, and height of the bed. Ensure that you measure both the interior and exterior dimensions, as this will impact the volume of soil required.
Multiplying the dimensions to find the volume
Once you have measured the dimensions of the raised bed, you can calculate its volume by multiplying the length, width, and height together. For example, if your raised bed measures 4 feet long, 3 feet wide, and 1 foot high, the volume would be 4 x 3 x 1 = 12 cubic feet.
Determining the compost needed based on bed volume
Recommended depth of compost
The depth of compost needed in a raised bed depends on several factors, including the specific needs of the plants you will be growing and the quality of your existing soil. In general, a depth of 6-12 inches of compost is recommended for optimum results. This depth allows for sufficient nutrient availability while also promoting healthy root development.
Calculating the volume of compost needed
To determine how much compost is needed based on the volume of the bed, multiply the volume by the desired depth of compost. For example, if your raised bed has a volume of 12 cubic feet and you want to add a 6-inch layer of compost, you would calculate 12 x 0.5 (6 inches in feet) = 6 cubic feet of compost needed.

Factors affecting the compost requirements
Soil type
The type of soil you have in your raised bed will affect the amount of compost needed. Sandy soils, for example, tend to be less fertile and require more compost to supplement nutrient levels. On the other hand, clay soils may already have a higher nutrient content and may require less compost. Conduct a soil test to determine the specific nutrient needs of your soil and adjust the compost requirements accordingly.
Crop selection
Different crops have different nutrient requirements, and this should be taken into account when determining how much compost is needed. For example, heavy-feeding plants like tomatoes and cucumbers may require a thicker layer of compost compared to low-feeding crops like lettuce and radishes. Consider the specific needs of the plants you plan to grow and adjust the compost requirements accordingly.
Gardening practices
Your gardening practices, such as crop rotation and intercropping, can also impact the compost requirements of your raised bed. Crop rotation involves planting different crops in the same bed each season to prevent nutrient depletion and disease buildup. Intercropping, on the other hand, involves planting multiple crops close together to maximize space and nutrient utilization. Both practices can affect the nutrient needs of your soil and, consequently, the amount of compost required.
Factors to consider when buying compost
Quality of compost
When buying compost, it is essential to consider its quality. High-quality compost should be dark and crumbly, with a pleasant earthy smell. Avoid compost that appears unfinished or contains large pieces of undecomposed material. Quality compost is rich in organic matter and beneficial microorganisms, ensuring that it provides maximum benefits to your raised bed.
Organic vs. inorganic compost
Another factor to consider is whether to use organic or inorganic compost. Organic compost is made from natural materials and does not contain synthetic additives or chemicals. Inorganic compost, on the other hand, may contain synthetic fertilizers or other chemical additives. While both types can provide nutrient benefits, organic compost is generally preferred as it promotes soil health and reduces the risk of chemical buildup over time.
Sourcing compost locally
Whenever possible, it is recommended to source compost locally. Local compost is often made from materials found in your region, which can help to improve soil structure and fertility. Additionally, buying compost locally supports local businesses and reduces the environmental impact associated with transporting compost over long distances.
Calculating the number of bags of compost required
Volume of compost in a bag
Compost is typically sold in bags, and the volume of each bag can vary depending on the supplier. Most bags of compost contain between 1 and 2 cubic feet of material. Check the packaging or contact the supplier to determine the specific volume of compost in each bag.
Dividing the total volume by bag volume
To determine how many bags of compost are needed, divide the total volume of compost required by the volume of compost in each bag. For example, if you need 6 cubic feet of compost and each bag contains 1 cubic foot, you would need 6 bags of compost.
Alternative methods to filling a raised bed with compost
Layering technique
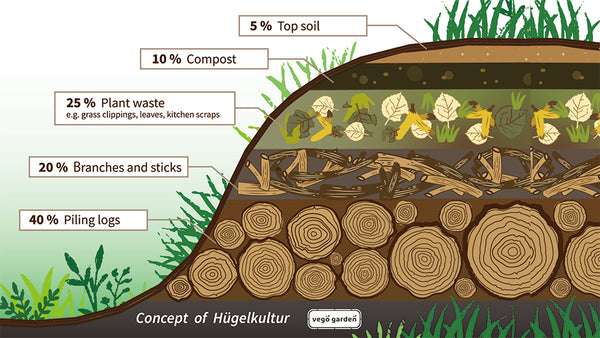
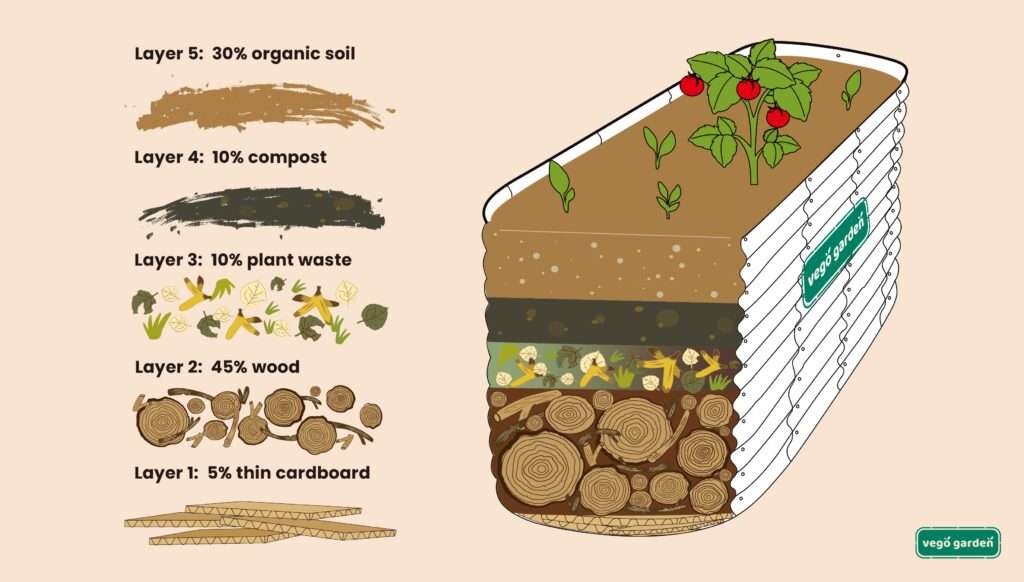
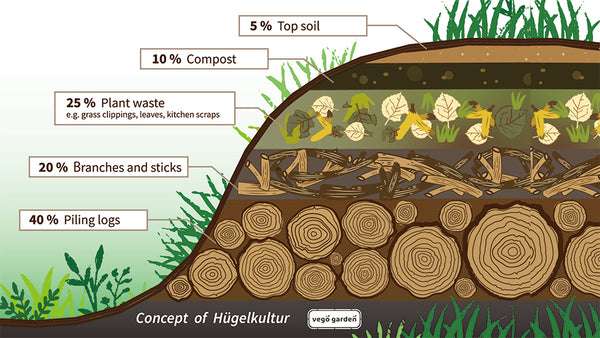
An alternative method to filling a raised bed with compost is the layering technique. This involves adding alternating layers of compost and other organic materials, such as grass clippings, leaves, or straw. The layers gradually decompose and form a nutrient-rich soil over time. This method is particularly useful if you have limited access to compost or want to incorporate other organic materials into your raised bed.
Combining compost with other materials
You can also combine compost with other materials to fill a raised bed. For example, you can mix compost with topsoil, garden soil, or other amendments like perlite or vermiculite to create a customized growing medium. This approach allows you to tailor the soil composition to the specific needs of your plants and ensures that your raised bed has a good balance of nutrients, drainage, and water retention.

Tips for successful compost application in a raised bed
Uniform distribution
When adding compost to a raised bed, ensure that it is evenly distributed throughout the bed. This will help to prevent nutrient imbalances and ensure that all plants have equal access to nutrients and moisture. Use a garden rake or shovel to spread the compost in a uniform layer, taking care not to disrupt the underlying soil.
Mixing compost with existing soil
To fully integrate the compost with the existing soil in the raised bed, consider mixing it thoroughly. This can be done using a garden fork or a tiller, depending on the size of the bed. Mixing the compost with the soil will promote better nutrient distribution and help to improve soil structure over time.
Applying compost at the right time
Timing is crucial when applying compost to a raised bed. Ideally, compost should be added before planting to allow sufficient time for it to break down and release nutrients. However, if you are working with an existing bed, you can apply compost during the growing season by gently incorporating it into the top few inches of soil without disturbing the plant roots.
Case studies of compost usage in raised beds
Real-life examples of compost requirements for different beds
To illustrate the varying compost requirements for different raised beds, let’s consider a few case studies:
Case Study 1: A small raised bed measuring 3 feet long, 2 feet wide, and 1 foot high. Based on the dimensions, the bed has a volume of 6 cubic feet. Assuming a recommended compost depth of 6 inches, the bed would require 3 cubic feet of compost.
Case Study 2: A larger raised bed measuring 8 feet long, 4 feet wide, and 1.5 feet high. The volume of the bed would be 48 cubic feet. With a desired compost depth of 12 inches, the bed would require 24 cubic feet of compost.
These case studies demonstrate how the size and dimensions of the raised bed impact the amount of compost needed. It is important to calculate the specific requirements for your own bed using the techniques outlined earlier.
Common mistakes to avoid when filling a raised bed with compost
Using low-quality compost
One common mistake is using low-quality compost that may contain weed seeds, pathogens, or harmful chemicals. Always choose compost from a reputable supplier and ensure that it meets quality standards. If in doubt, conduct a simple germination test by planting a few seeds in a sample of the compost to check for weed seeds.
Overfilling the bed with compost
Another mistake to avoid is overfilling the raised bed with compost. Although compost is beneficial for plant growth, it is important to maintain a proper balance between compost and soil. Overfilling the bed can lead to poor drainage and waterlogging, potentially damaging the roots of your plants. Stick to the recommended depth of compost based on your specific needs.
Conclusion
When it comes to filling a raised bed with compost, calculating the right amount is essential for successful gardening. By considering factors such as the volume of the bed, desired depth of compost, and specific nutrient requirements, you can determine how much compost is needed. Whether you choose to purchase compost in bags or explore alternative methods, such as layering or combining with other materials, incorporating compost into your raised bed will provide your plants with the essential nutrients they need for healthy growth. Happy gardening!