Newfoundland and Labrador, located in the eastern part of Canada, boasts a rich history and diverse landscapes. With a population of around 521k, the province is neither growing nor shrinking, mainly due to a declining fishing and mining industry. While off-grid living is not recommended in this province due to low population density and a high unemployment rate, there are incentives and rebates for solar and wind power systems. With untouched nature, reserves, and national parks, Newfoundland and Labrador offer a haven for wildlife enthusiasts. However, it’s important to note that the cost of living is higher than the national average, and job opportunities are limited, with an unemployment rate of 12.4%. Despite these challenges, discovering the unique landscapes and communities of Newfoundland and Labrador can be an enticing opportunity.

History
Settlement by Indigenous Peoples
Newfoundland and Labrador has a long and rich history of settlement by Indigenous peoples. The Beothuk and Mi’kmaq were the original inhabitants of the province, living off the land and engaging in fishing, hunting, and trading. They had a deep connection to the land and the sea, and their culture and traditions are still cherished and celebrated today.
European Exploration and Settlement
European exploration and settlement began in the late 15th century when John Cabot, an Italian explorer sailing under the English flag, landed on the shores of Newfoundland in 1497. This marked the beginning of European presence in the region. The French also established a foothold in the area, primarily in what is now Labrador.
The colony of Newfoundland was established by the English in the early 17th century, and over the years, European settlers from England, Ireland, and Scotland flocked to the province in search of new opportunities. These settlers brought with them their own traditions, customs, and ways of life, which have influenced the culture of Newfoundland and Labrador to this day.
Role in World Wars
Newfoundland and Labrador played a significant role in both World Wars. During World War I, the province heavily contributed to the war effort by sending soldiers, resources, and support to the front lines. The famous Royal Newfoundland Regiment, known for its bravery and sacrifice, fought alongside other Allied forces.
In World War II, Newfoundland was still a separate Dominion, separate from Canada. It was strategically important due to its location, serving as a crucial base for convoys crossing the Atlantic. The province was heavily involved in military operations, supplying troops, ships, and airfields.
Confederation with Canada
Newfoundland and Labrador joined the Canadian Confederation on March 31, 1949, after a referendum in which the majority of Newfoundlanders voted in favor of union with Canada. The decision was made to address economic and political challenges faced by the province at the time. The union brought new opportunities for development and growth, and the province became Canada’s tenth province.
Population and Economy
Population Size
The population of Newfoundland and Labrador is currently around 521,000 people. While this is a relatively small population compared to other provinces in Canada, it is important to note that the population has remained relatively stable in recent years. This means that the province is neither experiencing significant growth nor a decline in population.
Population Trends
Newfoundland and Labrador has faced challenges in retaining its population in recent years due to factors such as limited job opportunities and a high unemployment rate. Many young people have left the province in search of better opportunities elsewhere. However, efforts are being made to attract and retain residents through initiatives such as student loan forgiveness programs and incentives for skilled workers.
Economic Sectors
The economy of Newfoundland and Labrador has traditionally relied on fishing and mining. The province has a rich fishing history, with cod fishing being a major industry for many years. However, the cod fishery collapsed in the 1990s, leading to a decline in the fishing industry.
Mining has also played a significant role in the economy, with the province being rich in mineral resources such as iron ore, nickel, and copper. However, mining has also faced challenges in recent years, with fluctuations in commodity prices and environmental concerns impacting the industry.
Decline in Fishing and Mining
The decline in the fishing and mining industries has had a significant impact on the economy of Newfoundland and Labrador. Many communities that were once dependent on these industries have struggled to adapt and find alternative sources of employment. This has contributed to the high unemployment rate in the province.
Incentives for Solar and Wind Power Systems
In recent years, there has been an increased focus on renewable energy in Newfoundland and Labrador. The provincial government has implemented incentives and rebates for the installation of solar and wind power systems. These incentives aim to promote the use of clean energy sources and reduce reliance on traditional energy sources.
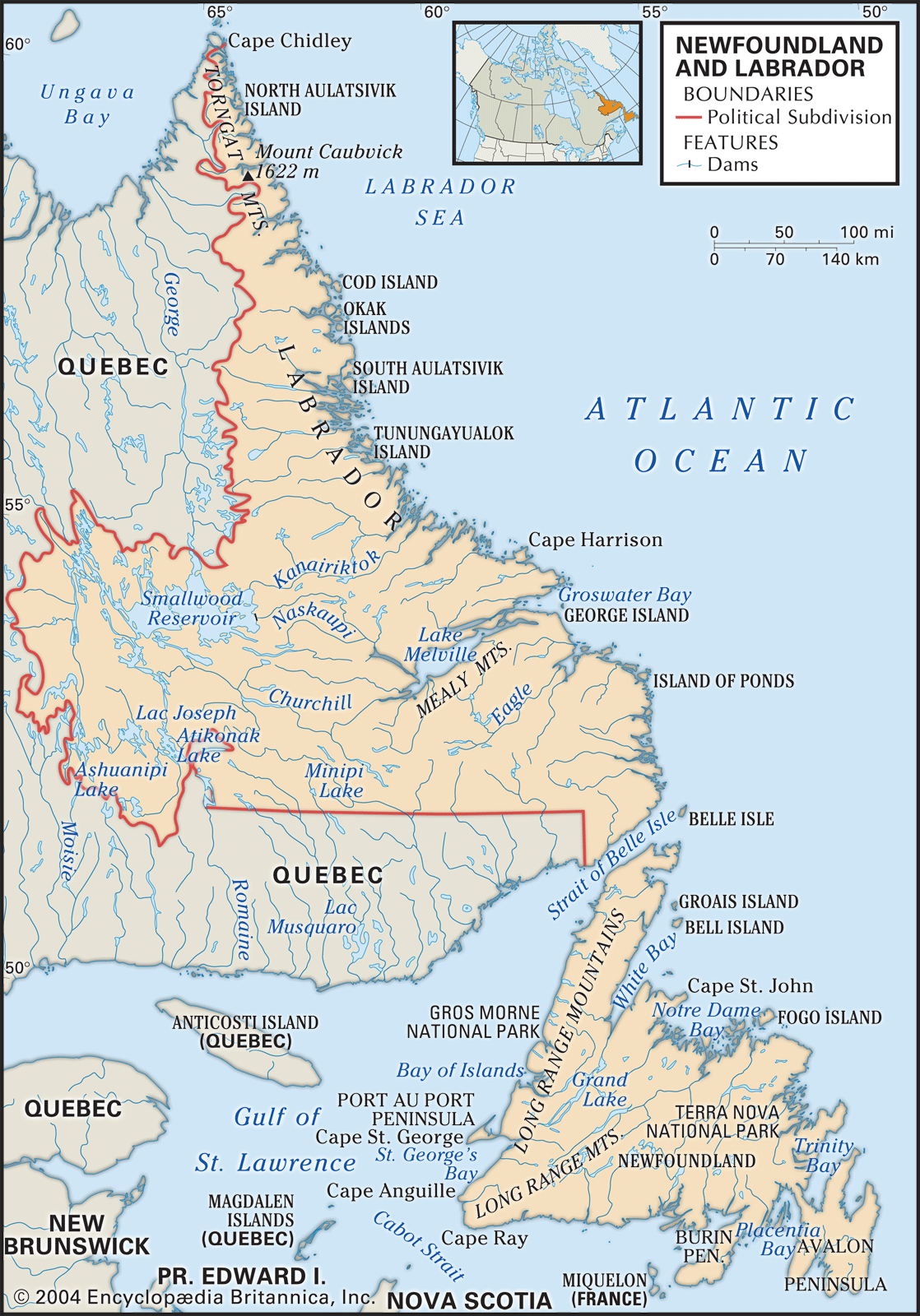
Geography
Population Density
Newfoundland and Labrador has a relatively low population density compared to other provinces in Canada. With most of the population residing in Newfoundland, there are vast areas of untouched wilderness in Labrador. This low population density contributes to the province’s unique charm and offers opportunities for those seeking a quieter and more secluded lifestyle.
Major Cities
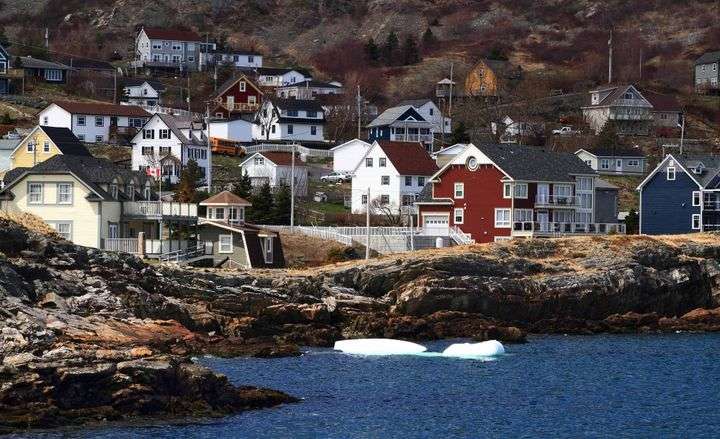
The biggest cities in Newfoundland and Labrador are St. John’s, Conception Bay South, Mount Pearl, Paradise, and Corner Brook. St. John’s, the capital city, is known for its vibrant culture, colorful row houses, and stunning coastal landscapes. These cities offer a range of amenities and services, while still maintaining a small-town feel.
Natural Reserves and National Parks
Newfoundland and Labrador boast numerous natural reserves and national parks, showcasing the province’s untouched nature and diverse ecosystems. Gros Morne National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a must-visit for nature enthusiasts with its towering fjords, ancient mountains, and unique geological features. Other notable parks include Terra Nova National Park, Torngat Mountains National Park, and Cape St. Mary’s Ecological Reserve.
Climate
The climate in Newfoundland and Labrador can vary significantly between different regions. Labrador experiences a humid continental climate, characterized by cold winters and mild summers. In the northern parts of Newfoundland, a subarctic climate prevails, with cooler temperatures and shorter summers. The southern parts of Newfoundland enjoy a milder, more moderate climate.
Crop Growth and Water Availability
The province’s climate, particularly in Labrador, poses challenges to crop growth. The short growing season and cool temperatures limit the types of crops that can be cultivated successfully. However, in the southern parts of Labrador, the climate is more favorable for growing crops, and farmers have found success with crops such as root vegetables, berries, and small grains.
Water availability is generally not a concern in Newfoundland and Labrador, with plenty of fresh water sources throughout the province. Most of the water is clean and suitable for drinking and agricultural purposes.
Wildlife
Newfoundland and Labrador are home to a rich and diverse array of wildlife. The province’s vast forests, rivers, and coastal areas provide habitats for a wide range of species. Caribou, lynx, muskrat, foxes, bears, moose, and various fish species can be found in the province. Birdwatchers will also delight in the opportunity to spot puffins, bald eagles, and other migratory bird species.
Off-Grid Living
Legal Status of Off-Grid Living
Living off the grid is legal in Newfoundland and Labrador. The province recognizes that some individuals may choose to live a self-sufficient lifestyle and has not imposed restrictions on off-grid living. However, it is important to research and understand local regulations and requirements to ensure compliance with building codes, health and safety standards, and environmental regulations.
Accessibility and Road Conditions
While Newfoundland and Labrador offer breathtaking landscapes and natural beauty, it is important to note that road access can be limited in certain areas, especially during winter. Snowstorms and ice can make roads impassable, and it is crucial to be prepared and have appropriate transportation and supplies for remote living.
Cost of Land and Living
The cost of land and living in Newfoundland and Labrador is generally higher than the national average. Remote locations and limited infrastructure can make accessing goods and services more expensive. Additionally, the cost of land can vary depending on location and size. It is important to take these factors into consideration when planning for off-grid living in the province.
Unemployment Rate
Newfoundland and Labrador currently has a high unemployment rate of 12.4%. Limited job opportunities, particularly in rural areas, can make it challenging for individuals seeking employment. It is important to have alternative sources of income or savings when considering off-grid living in the province.
Natural Disasters
Newfoundland and Labrador are susceptible to a range of natural disasters, including earthquakes, storms, floods, tornadoes, hurricanes, wildfires, and tsunamis. It is essential to be prepared and have emergency plans in place when living off the grid in the province. Understanding local weather patterns and evacuation routes is crucial for ensuring the safety and well-being of residents.
Living Off the Grid
Feasibility and Considerations
Living off the grid in Newfoundland and Labrador is feasible, but it requires careful planning, research, and consideration of various factors. Access to basic amenities such as water, electricity, and waste disposal can be challenging in remote areas. It is important to assess the feasibility of self-sufficiency based on individual needs and requirements.
Affordability in Rural Areas
Rural areas of Newfoundland and Labrador may offer more affordable options for off-grid living compared to larger cities. Lower land prices and reduced living costs can make rural living more financially viable. However, it is crucial to factor in the cost of infrastructure, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and off-grid living systems, when considering the overall affordability of off-grid living in the province.
Regulations and Requirements
While living off the grid is legal in Newfoundland and Labrador, residents must adhere to local regulations and requirements. These may include building codes, health and safety standards, and environmental regulations. It is essential to research and understand these requirements to ensure compliance and avoid any potential legal issues.
Varying Costs of Living
The cost of living can vary across Newfoundland and Labrador. Rural areas typically have lower living costs due to reduced infrastructure and access to services. However, it is important to consider additional expenses such as transportation, emergency supplies, and maintenance of off-grid living systems. Creating a detailed budget and financial plan is crucial for determining the overall costs of off-grid living in the province.
Diverse Landscapes and Communities
Newfoundland and Labrador offer diverse landscapes and communities for those seeking off-grid living. From rugged coastlines to picturesque lakes and forests, the province has something to offer every nature enthusiast. Smaller communities in remote areas provide opportunities for a close-knit community and a simpler way of life. It is important to research and visit different regions to find the perfect fit for off-grid living in Newfoundland and Labrador.
In conclusion, Newfoundland and Labrador provide a unique opportunity for those considering off-grid living. With its rich history, stunning landscapes, and vast natural resources, the province offers a chance to embrace a self-sufficient lifestyle. However, careful planning, research, and understanding of local regulations and requirements are essential to ensure a successful and sustainable off-grid living experience.