In this article, we will be discussing the ideal depth for raised garden beds. Whether you’re an off-grid living enthusiast or simply passionate about gardening, understanding the right depth for your garden beds is crucial. We’ll explore the factors that influence the ideal depth and why it matters, as well as provide helpful tips to ensure your plants thrive. By the end, you’ll have a better understanding of how to create the perfect growing environment for your garden. Let’s get started!
The Ideal Depth for Raised Garden Beds
If you are an avid gardener or someone interested in starting your own garden, then you have probably come across the concept of raised garden beds. Raised garden beds offer numerous benefits, such as improved soil drainage, easier access and maintenance, and enhanced garden organization. However, when it comes to the ideal depth for raised garden beds, there are several factors to consider. In this article, we will explore the recommended depth for raised garden beds, the advantages of shallow and deeper beds, optimal depth for specific plants, and additional considerations for successful gardening.
Improved Soil Drainage
One of the primary benefits of raised garden beds is improved soil drainage. By elevating the soil level, raised beds prevent excess water from pooling, which can lead to waterlogging and poor root health. The ideal depth of a raised garden bed contributes significantly to proper drainage.
Easier Access and Maintenance
Another advantage of raised garden beds is the ease of access and maintenance. The raised height of these beds eliminates the need to bend over or kneel down, making gardening tasks more comfortable and accessible for individuals with physical limitations. The ideal depth for raised garden beds should consider the gardener’s physical abilities, ensuring that they can easily reach and tend to their plants.
Enhanced Garden Organization
Raised garden beds also provide an opportunity for enhanced garden organization. With defined borders and contained soil, raised beds help delineate different planting areas and prevent plants from encroaching on each other. Additionally, the ideal depth of raised garden beds allows for better separation of plants with varying root depths or growth habits.
Type of Plants Being Grown
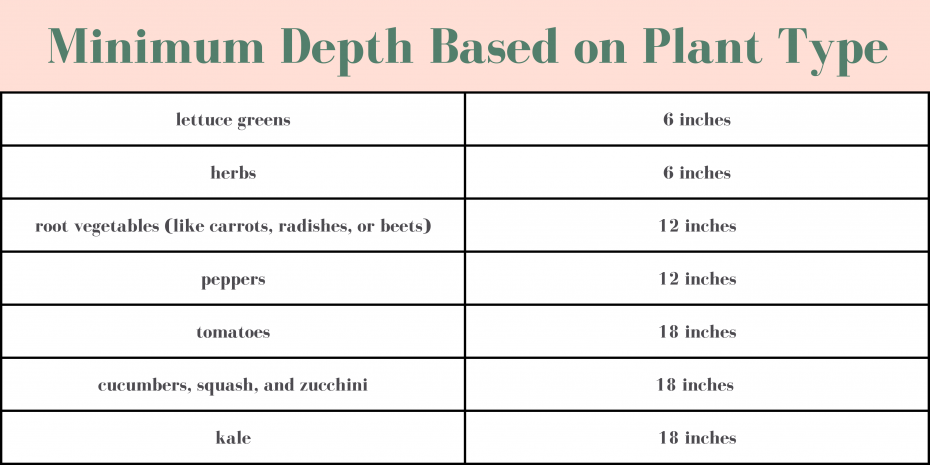
When determining the ideal depth for raised garden beds, it is essential to consider the type of plants you will be growing. Shallow-rooted vegetables, such as lettuce, radishes, and spinach, thrive in shallower beds ranging from 6 to 8 inches deep. In contrast, deep-rooted vegetables like tomatoes, carrots, and potatoes require deeper beds of 12 to 18 inches to accommodate their extensive root systems.

Environmental Factors
In addition to the type of plants, you should also take into account the environmental factors of your garden. For example, if you live in an area with heavy rainfall, deeper beds can help prevent waterlogging and ensure proper drainage. On the other hand, if you live in a particularly dry climate, shallow beds might be more suitable to retain moisture.
Gardener’s Physical Abilities
Your own physical abilities as a gardener should not be overlooked when determining the ideal depth for raised garden beds. If you have limited mobility or find it challenging to bend over for extended periods, shallower beds that are easier to reach into might be a better choice. It is crucial to prioritize your comfort and enjoyment when planning your garden.

Recommended Depth for Raised Garden Beds
While the ideal depth for raised garden beds can vary depending on the factors mentioned above, there are some general guidelines to consider. For most plants, a minimum depth of 6 to 8 inches is sufficient. This depth allows for proper root development and plant growth, especially for shallow-rooted vegetables and herbs.
Shallow Beds vs. Deeper Beds
Both shallow and deeper beds have their advantages, and choosing the appropriate depth depends on your specific gardening needs and goals.
Advantages of Shallow Beds
Shallow beds are easier to construct and require less soil filling. They also warm up faster in the spring, allowing for earlier planting. Shallow beds are ideal for plants with shallow root systems and those that prefer well-draining soil conditions, such as leafy greens and herbs.
Advantages of Deeper Beds
Deeper beds provide more room for root development and are suitable for plants with extensive root systems. They retain moisture better and can offer better insulation during colder months. Deeper beds also allow for layering of different soil types and amendments, creating optimal growing conditions.
Considerations for Choosing Depth
When deciding between shallow and deeper beds, consider the types of plants you will be growing, your gardening goals, and the environmental conditions in your area. It is also important to ensure that the chosen depth is manageable for you in terms of accessing and maintaining your garden.

Optimal Depth for Specific Plants
While general guidelines provide a good starting point, certain plants have specific depth requirements for optimal growth and productivity. Here are some examples:
Shallow-Rooted Vegetables
Shallow-rooted vegetables like lettuce, radishes, and spinach can thrive in raised beds with a depth of 6 to 8 inches. These plants have shallower root systems and do not require as much soil depth.
Deep-Rooted Vegetables
Deep-rooted vegetables such as tomatoes, carrots, and potatoes need raised beds with depths ranging from 12 to 18 inches. These plants develop extensive root systems and require more space to grow and access nutrients.
Herbs and Flowers
Herbs and flowers, depending on their variety, may have varied root depths. However, most commonly grown herbs and flowers can do well in raised beds with depths similar to shallow-rooted vegetables, ranging from 6 to 8 inches.
Gardening in Limited Spaces
For individuals with limited gardening space or those unable to accommodate deeper beds, there are alternative options that can still allow for successful gardening.
Alternative Options for Limited Depth
If space limitations prevent you from creating deeper beds, consider alternative gardening techniques such as container gardening or vertical gardening. These methods allow you to grow a variety of plants in smaller spaces while still providing adequate soil depth for their root systems.
Container Gardening
Container gardening involves planting in pots or containers that can be placed on patios, balconies, or even windowsills. This method allows for complete control over soil depth and provides flexibility in terms of moving plants around or bringing them indoors during harsh weather conditions.
Vertical Gardening
Vertical gardening utilizes vertical wall space to grow plants vertically, using structures such as trellises, hanging baskets, or vertical planters. This technique maximizes space and can be suitable for growing vining plants, flowers, or even vegetables.

Importance of Soil Quality
Regardless of the depth you choose for your raised garden beds, soil quality is of utmost importance for successful gardening. Proper soil composition, amendment, and maintenance are crucial factors to consider.
Proper Soil Composition
The soil used in raised garden beds should be a well-balanced mixture of topsoil, compost, and other organic matter. This combination provides essential nutrients, good drainage, and a suitable environment for root development.
Amending Soil in Raised Beds
Over time, soil nutrients can become depleted, especially in raised garden beds where plant roots have limited access to external soil. Regularly amending the soil with compost, organic matter, and balanced fertilizers helps maintain soil fertility and ensures that your plants have access to the necessary nutrients.
Maintaining Soil Fertility
Soil fertility can be maintained by practices such as crop rotation, which involves changing the types of plants grown in raised beds each season. Additionally, cover cropping during the off-season helps improve soil structure, prevent erosion, and adds organic matter to the soil.
Preventing Common Issues
While raised garden beds offer numerous advantages, there are some common issues to be aware of and take preventive measures against.
Waterlogging and Poor Drainage
Raised beds can still experience waterlogging and poor drainage if the soil used does not provide adequate porosity and drainage. To prevent this, ensure that your soil mix is well-draining and consider incorporating materials like perlite or vermiculite. In extreme cases, installing a drainage system in the bottom of the raised bed can help redirect excess water.
Weed Growth and Root Competition
Weeds can still find their way into raised garden beds, competing with your plants for nutrients and resources. Regular weeding and mulching can help prevent weed growth and minimize root competition. Mulching also helps retain moisture, regulate soil temperature, and improve overall soil health.
Soil Erosion and Compaction
Raised beds, especially those with shallow depths, are susceptible to soil erosion and compaction over time. To prevent erosion, consider incorporating appropriate ground cover plants or using materials like mulch or straw to protect the soil surface. Avoid compression of the soil by minimizing foot traffic within the raised beds and using stepping stones or paths around them.
Additional Considerations
In addition to depth and soil quality, there are several other factors to consider when planning and maintaining raised garden beds.
Raised Bed Construction Materials
When constructing raised garden beds, choose materials that are durable, non-toxic, and suitable for your gardening needs. Options range from wood and metal to concrete blocks or bricks. Each material has its own benefits and drawbacks, so consider factors such as cost, appearance, and longevity.
Integrating Irrigation Systems
Efficient watering is essential for the success of raised garden beds. Consider integrating an irrigation system, such as drip irrigation, to ensure that your plants receive consistent water supply while minimizing water wastage. This can be especially useful during hot summer months when watering needs increase.
Crop Rotation and Bed Maintenance
To prevent the buildup of pests and diseases, practice crop rotation by changing plant families in each raised bed from season to season. Additionally, regular maintenance tasks such as pruning, harvesting, and removing dead plants help maintain a healthy growing environment and maximize productivity.
Maximizing Yield and Efficiency
To maximize yield and efficiency in your raised garden beds, consider implementing various techniques and strategies.
Companion Planting Strategies
Companion planting involves growing compatible plants together to enhance growth and repel pests naturally. By carefully selecting plant combinations, you can increase yields, deter pests, and improve overall garden health.
Proper Spacing and Plant Density
Ensure proper spacing between plants to allow for adequate air circulation and prevent overcrowding. Overcrowding can lead to increased competition for nutrients, limited sunlight penetration, and higher susceptibility to diseases. Follow spacing recommendations specific to each plant variety for optimal results.
Mulching and Composting
Mulching provides multiple benefits such as weed suppression, moisture regulation, and soil temperature moderation. Additionally, incorporating compost into your raised beds enriches the soil with organic matter and essential nutrients, improving plant health and productivity.
Conclusion
Understanding the ideal depth for raised garden beds is crucial for successful gardening. By considering various factors such as the type of plants being grown, environmental factors, and your own physical abilities, you can create optimal growing conditions to maximize yields and enhance the beauty of your garden. With the right depth, proper soil composition, and maintenance practices, raised garden beds can provide an enjoyable and fruitful gardening experience.




