Hello there! Today, we’re going to explore the fascinating topic of whether clay can keep things cold. We’ll take a closer look at the concept of off-grid living and discover how clay may play a role in preserving cool temperatures. So, if you’ve ever wondered about the potential of clay to keep things chilly, stick around, and let’s uncover the facts together!
Can clay keep things cold?
Off-grid living has become increasingly popular in recent years as people seek a more sustainable and self-sufficient lifestyle. Living off the grid means disconnecting from public utilities such as water, electricity, and gas, and instead relying on renewable energy sources like solar panels, wind turbines, and rainwater harvesting. One of the biggest challenges faced by off-grid dwellers is the lack of access to modern amenities, including refrigeration. Refrigeration is crucial for preserving food, especially in areas without electricity. This brings us to the question: can clay keep things cold?
Defining Off-Grid Living
Before we delve into the potential of clay for cold storage, let’s first define what off-grid living entails. Off-grid living refers to a lifestyle where individuals or communities are self-sufficient and do not rely on public utilities. This can involve generating their own electricity, sourcing water from natural sources, and cultivating their own food. Off-grid living offers numerous benefits, including reduced environmental impact, increased resilience to power outages, and a sense of independence.
Benefits of Off-Grid Living
Living off the grid offers a plethora of advantages. Firstly, it allows individuals to reduce their carbon footprint by minimizing their reliance on fossil fuels. Off-grid dwellers often use renewable energy sources like solar power or wind turbines, resulting in decreased greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, off-grid living promotes self-sufficiency, enabling individuals to rely on their own resources rather than depending on outside systems. This can lead to enhanced resilience during emergencies or natural disasters when public services may be disrupted. Moreover, off-grid living encourages a closer connection to nature and fosters a simpler, more sustainable way of life.
Challenges of Off-Grid Living
While there are numerous benefits to off-grid living, it also presents its fair share of challenges. One of the major challenges is the absence of conventional amenities. Refrigeration, in particular, is crucial for preserving food, medications, and other perishable items. Without access to electricity, off-grid dwellers often face difficulties in storing these items safely for extended periods. This is where alternative cooling methods, such as clay cooling, come into the picture.
Understanding Cold Storage
Cold storage refers to the process of maintaining low temperatures to preserve perishable items, preventing them from spoiling or decaying. In traditional refrigeration systems, electricity is used to remove heat from the storage area, creating a cool environment. However, in off-grid scenarios, electricity may not be readily available. This necessitates the exploration of alternative cooling solutions that don’t rely on electricity.

Significance of Cold Storage in Off-Grid Living
Cold storage plays a vital role in off-grid living as it allows individuals to store and preserve food items for extended periods, reducing waste and ensuring a constant food supply. By effectively preserving food, off-grid dwellers can overcome the challenges of limited access to grocery stores and maintain a diversified and nutritious diet. Additionally, cold storage is crucial for storing medications that require specific temperature conditions, ensuring the health and well-being of individuals living off the grid.
Properties and Composition of Clay
Clay is a natural material that has been used for various applications for thousands of years. It is composed of fine particles of minerals, organic matter, and water. Clay has unique properties that make it suitable for a range of uses, including its ability to retain moisture, plasticity, and insulation capabilities. These properties make clay a promising candidate for cold storage solutions in off-grid living.
Various Applications of Clay
Clay has been utilized for a wide range of applications, from pottery and construction to medicinal purposes and soil improvement. Its versatility and abundance have made it a valuable resource throughout human history. In recent years, clay’s insulating and cooling properties have gained attention in off-grid communities seeking sustainable and efficient ways to keep things cold.
Principles of Clay’s Cooling Properties
Clay’s cooling properties revolve around the principles of evaporation and thermal insulation. When water evaporates from a clay surface, it absorbs heat from its surroundings, leading to a drop in temperature. This phenomenon, known as evaporative cooling, is the underlying principle behind clay’s ability to keep things cold. Additionally, clay’s dense composition acts as an effective insulator, reducing heat transfer and preventing temperature fluctuations.

Insulating and Thermal Capacities of Clay
Clay’s insulating properties stem from its high thermal capacity and low thermal conductivity. The thermal capacity of a material refers to its ability to absorb and store heat, while thermal conductivity measures its ability to conduct heat. Clay’s high thermal capacity enables it to absorb and retain heat, resulting in a gradual release of energy over time. Additionally, its low thermal conductivity minimizes the transfer of heat from the external environment, ensuring a stable and cool interior.
Advantages of Clay Over Other Cooling Materials
Clay offers several advantages over other cooling materials, especially in off-grid living scenarios. Unlike conventional refrigeration systems that require electricity, clay-based cooling solutions do not rely on external power sources. This makes clay a cost-effective and sustainable alternative for keeping things cold. Moreover, clay is widely available and accessible, making it suitable for communities with limited resources. Its natural composition also ensures that clay cooling solutions have minimal environmental impact.
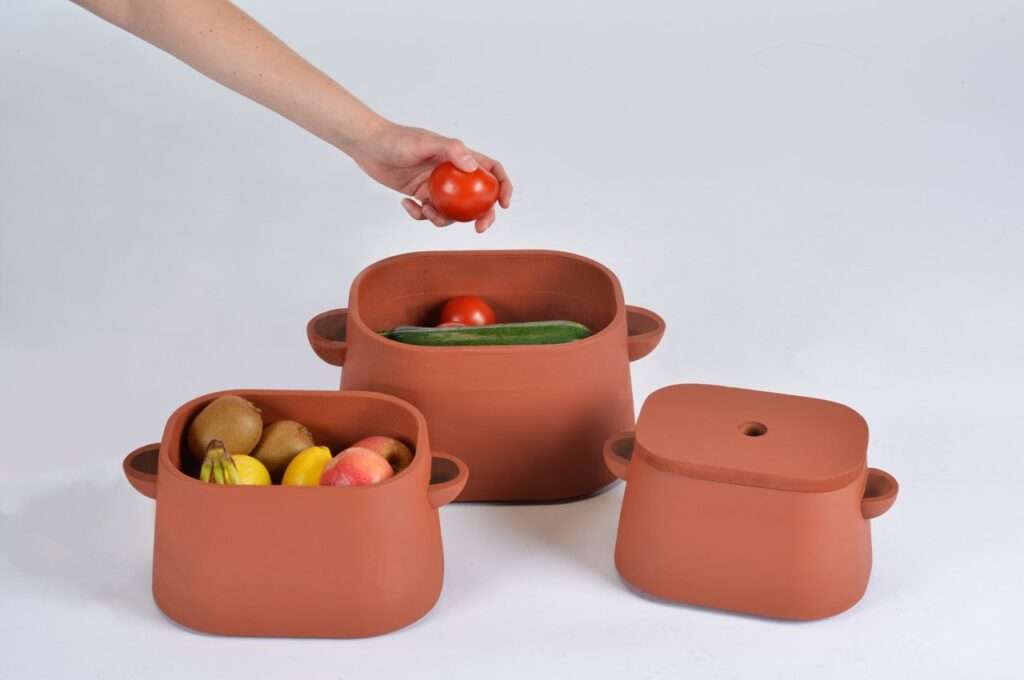
Clay Pots and Containers
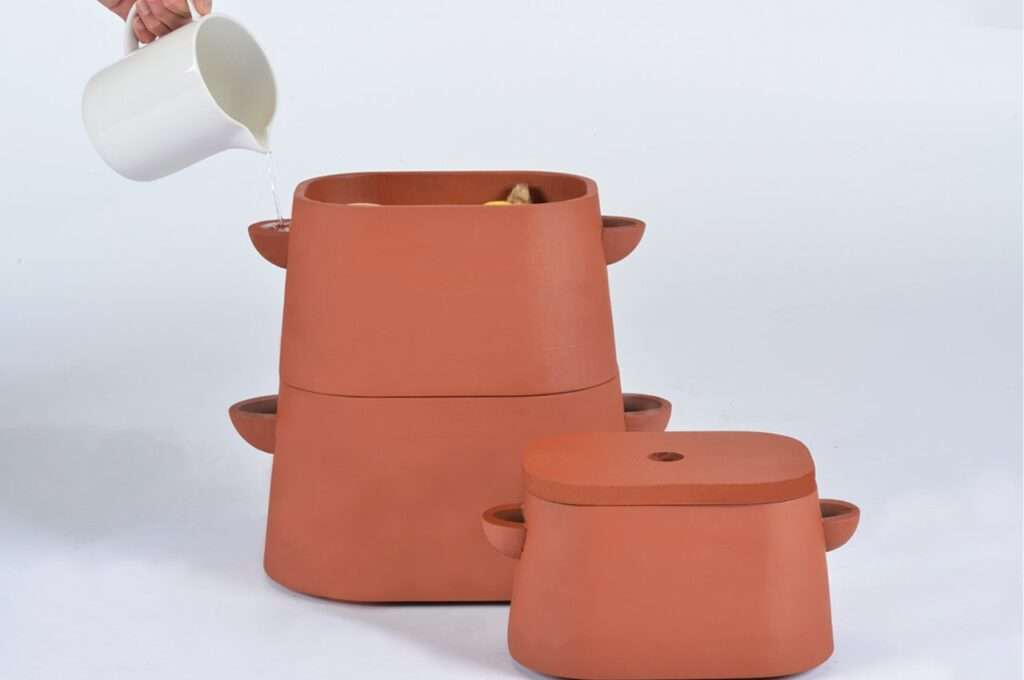
One of the simplest and most accessible ways to utilize clay for cold storage is through clay pots and containers. Clay pots have long been used for storing perishable items such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. The porous nature of clay allows water to evaporate slowly, cooling the contents of the pot. By placing the clay pot in a cool, shaded area, individuals can harness the evaporative cooling properties of clay to keep their food items fresh for longer periods.
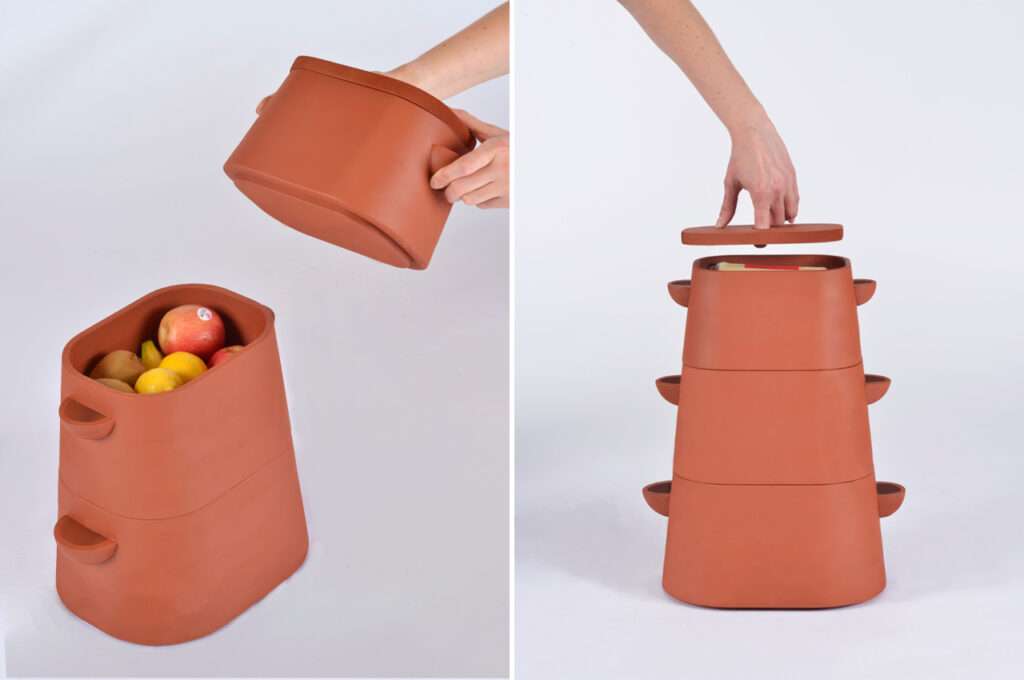
Clay Refrigerators and Coolers
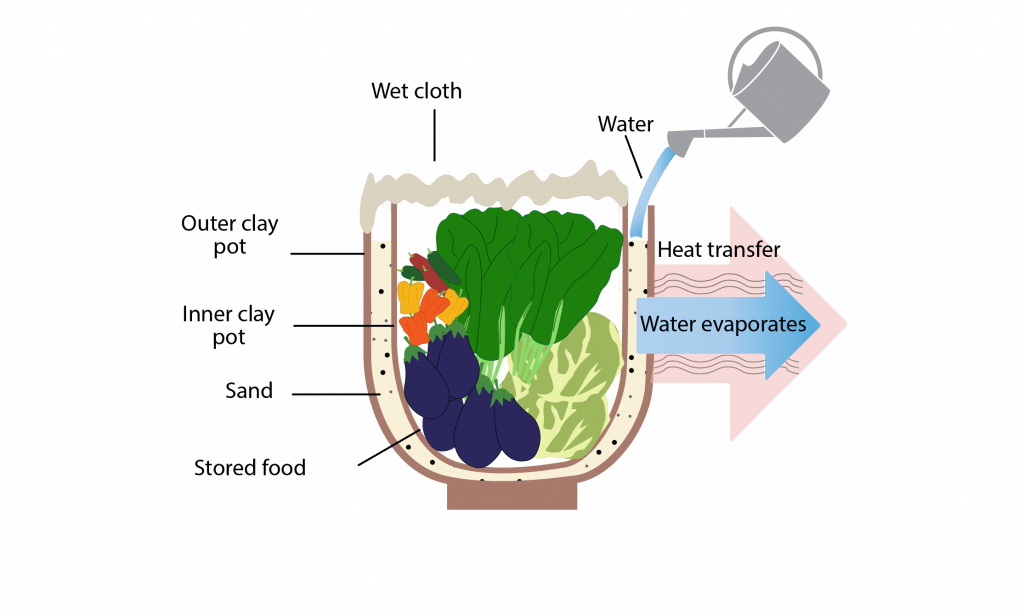
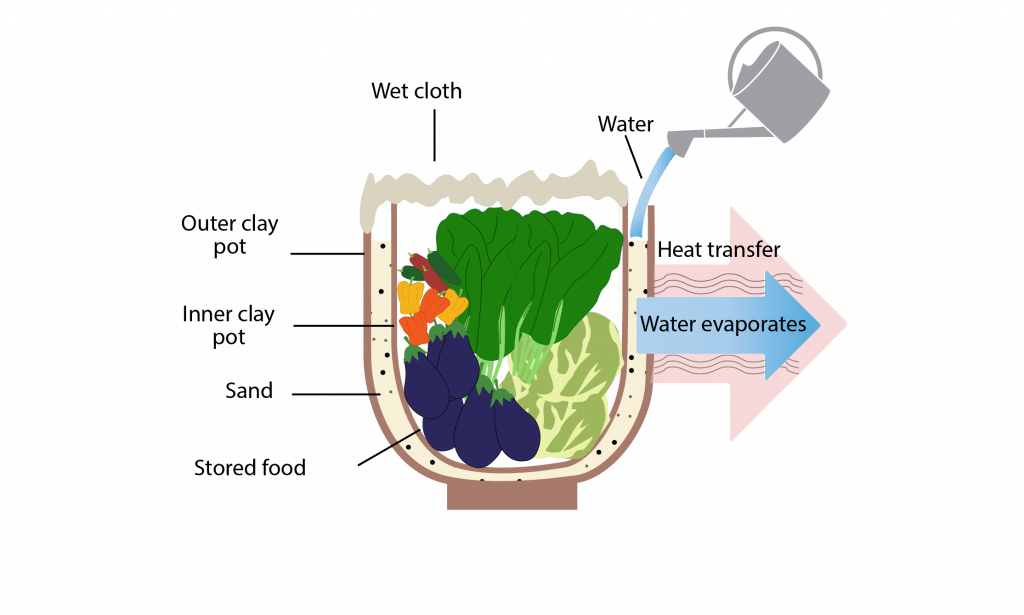
Innovations in clay refrigerators and coolers have further expanded the possibilities of clay-based cold storage. These devices utilize the insulating properties of clay to create a cool environment without the need for electricity. Clay refrigerators typically consist of two interconnected chambers, with the inner chamber made of clay and the outer chamber filled with a moist material such as sand. The evaporation of water from the outer chamber cools the inner clay chamber, providing a consistent and low-temperature environment for food storage.

Clay Cellars and Root Cellars
Clay cellars and root cellars have been a traditional method of storing fruits, vegetables, and other perishable items for centuries. These underground storage spaces take advantage of the natural cooling properties of clay, providing a stable and cool environment even in hot climates. The thick clay walls and the earth surrounding the cellar act as thermal insulation, preserving a low temperature and moisture levels. Clay cellars can be built above or below ground, depending on the availability of space and individual preferences.
Step-by-Step Guides for Building Clay Cold Storage Units
Building clay-based cold storage units can be a rewarding and practical project for individuals living off the grid. While the exact construction process may vary depending on the specific design and requirements, here is a general step-by-step guide to building a simple clay pot cooler:
- Select a clay pot with a wide base and a lid.
- Soak the pot in water for several hours or overnight, ensuring the clay is fully saturated.
- Fill the bottom of the pot with a layer of sand or gravel.
- Place a smaller clay pot, partially filled with water, in the center of the larger pot.
- Surround the smaller pot with ice or cool water.
- Cover the larger pot with the lid to create a sealed environment.
- Store perishable items inside the smaller pot, ensuring they are completely submerged in the water.
- Place the clay pot cooler in a cool, shaded area, away from direct sunlight.
This simple clay pot cooler utilizes the evaporation of water from the smaller pot’s surface to create a cool environment for the stored items. Regularly replenishing the ice or cool water helps maintain the temperature inside the cooler.
Clay as a Renewable and Eco-Friendly Material
One of the key advantages of clay cooling solutions is its sustainability and minimal environmental impact. Clay is a renewable resource that can be found abundantly in nature, requiring minimal processing or energy-intensive manufacturing. Its natural composition also means that clay cooling units can be safely disposed of without causing harm to the environment. By choosing clay-based cooling solutions, individuals can reduce their ecological footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Reducing Energy Consumption with Clay Cooling Solutions
In addition to their environmental benefits, clay cooling solutions also help reduce energy consumption. Traditional refrigeration systems are energy-intensive, consuming a significant amount of electricity. By opting for clay-based cold storage, off-grid dwellers can minimize their reliance on electricity and reduce their energy consumption. This not only leads to cost savings but also promotes a more sustainable way of living.

Ideal Clay Types and Mixtures
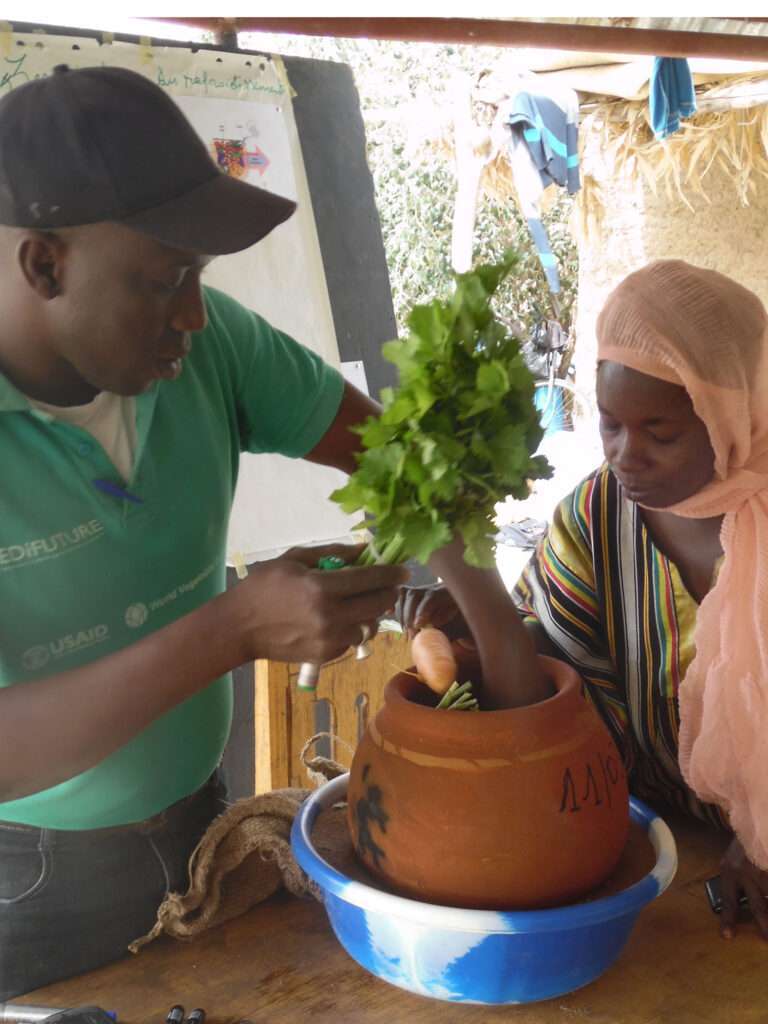
While clay offers numerous benefits for cold storage, not all clay types are equally suitable. The ideal clay for cooling applications should possess a high thermal capacity, low thermal conductivity, and good moisture retention properties. Clay with a higher proportion of fine particles tends to have better insulating capabilities. Adding organic matter, such as straw or sawdust, to the clay mixture can further enhance its insulation properties.
Proper Insulation and Ventilation
Insulation and ventilation are crucial considerations when using clay for cold storage. Proper insulation helps maintain a stable temperature inside the clay cooling unit, minimizing heat transfer from the external environment. This can be achieved by using thicker clay walls, adding insulation layers like straw or foam, or burying the storage unit underground. Ventilation is also important to prevent excessive humidity buildup, which can negatively impact the stored items. Properly designed vents or air circulation systems can help regulate moisture levels and ensure optimal storage conditions.
Maintenance and Care of Clay Cold Storage
Like any other material, clay cooling units require regular maintenance and care to ensure their effectiveness and longevity. Regular cleaning of the storage unit helps prevent the growth of mold or bacteria. Applying a food-safe sealant or wax to the clay surface can enhance its durability and resistance to moisture. It is also important to monitor the temperature and humidity levels within the storage unit to ensure optimal conditions for food preservation.
Experiences of Individuals and Communities Using Clay for Cold Storage
Many individuals and communities around the world have successfully implemented clay-based cold storage solutions in their off-grid lifestyles. The experiences and success stories of these pioneers can provide valuable insights and inspiration for others seeking to adopt similar methods. From small-scale clay pot coolers to large underground cellars, these individuals have demonstrated the practicality and effectiveness of clay cooling in various contexts and climates.
Humidity and Moisture Management
One of the challenges faced when using clay for cold storage is humidity and moisture management. Clay has a natural affinity for water and can absorb and release moisture, depending on the surrounding conditions. Excessive humidity can lead to mold growth or spoilage of the stored items. Proper ventilation and moisture control measures, such as installing vents or using desiccants, can help mitigate these issues and maintain an optimal storage environment.
Durability and Fragility of Clay
Clay, being a natural material, has inherent limitations in terms of durability and fragility. While it can be a sturdy and long-lasting material when properly maintained, it is susceptible to cracks, chipping, and breakage if mishandled or exposed to excessive force. Care should be taken when constructing and using clay cooling units to prevent damage and ensure their longevity.
Limitations in Cooling Efficiency
While clay cooling solutions offer many benefits, it is important to acknowledge their limitations in terms of cooling efficiency. Clay-based cooling relies on evaporative cooling, which is dependent on ambient conditions such as temperature and humidity. In hot and dry climates, clay cooling may be more effective than in humid or tropical environments. It is crucial to understand the local climate and adapt clay cooling techniques accordingly to maximize their efficiency.
Adapting Clay Cooling Solutions to Varying Climate Conditions
The effectiveness of clay cooling solutions can vary depending on the climate conditions in a particular area. Hot and dry climates are more conducive to clay-based cooling due to the high evaporation rates and low humidity levels. In humid or tropical environments, additional measures may be necessary to prevent excessive moisture buildup and ensure proper food preservation. These measures can include improved insulation, enhanced ventilation systems, or utilizing alternative cooling methods in conjunction with clay.
Cost-Effectiveness of Clay Cooling
One of the significant advantages of clay cooling solutions is their cost-effectiveness, particularly in comparison to conventional refrigeration systems. Clay is an affordable and widely available material, making it easily accessible for individuals with limited resources. Additionally, clay cooling solutions do not require electricity, resulting in significant cost savings in terms of energy consumption. This affordability and cost-effectiveness make clay cooling an attractive option for off-grid dwellers seeking sustainable and budget-friendly cold storage solutions.
Affordability and Accessibility of Clay Solutions
Clay cooling solutions offer affordability and accessibility for individuals and communities living off the grid. Clay is a globally available material, found in various regions around the world. Its accessibility makes it a viable option for off-grid dwellers, regardless of their geographical location. Moreover, clay cooling units can be constructed using basic tools and materials, further reducing costs and ensuring accessibility for all.
Clay’s Potential in Revolutionizing Cold Storage
Clay has the potential to revolutionize cold storage in off-grid living scenarios. Its natural cooling properties, availability, and sustainability make it an attractive alternative to traditional refrigeration systems. By harnessing the insulating and evaporative cooling capabilities of clay, off-grid dwellers can effectively preserve food, reduce waste, and enhance their self-sufficiency.
Balancing Clay Cooling with Modern Refrigeration
While clay cooling solutions offer numerous benefits, it is important to acknowledge that they may not completely replace modern refrigeration methods in certain contexts. Modern refrigeration systems provide precise temperature control and are necessary for storing certain items that require extremely low temperatures. However, clay cooling can supplement traditional refrigeration methods, especially in off-grid situations where access to electricity is limited or unreliable.
Recommendations for Further Research and Implementation
The potential of clay cooling in off-grid living warrants further research and implementation efforts. Exploring different clay types, mixtures, and designs can help optimize the cooling efficiency of clay-based cold storage units. Additionally, conducting studies on the long-term performance and durability of clay cooling solutions can provide valuable insights for future implementation. Collaboration between researchers, off-grid communities, and traditional knowledge holders can further enhance the practicality and effectiveness of clay cooling methods.
In conclusion, clay has shown promising potential in keeping things cold, making it a viable option for off-grid dwellers seeking sustainable and cost-effective cold storage solutions. Clay’s natural cooling properties, accessibility, and minimal environmental impact make it an attractive alternative to conventional refrigeration systems. By harnessing the principles of evaporative cooling and insulation, clay cooling units can effectively preserve food and other perishable items, enhancing the self-sufficiency and resilience of off-grid communities. While clay cooling may not completely replace modern refrigeration methods in all contexts, it provides a valuable and practical option for individuals seeking to live off the grid. With further research and implementation, clay cooling has the potential to revolutionize cold storage and contribute to a more sustainable future.