In this article, we will explore the topic of raised bed soil versus potting soil and help you understand the differences between the two. Whether you’re an avid gardener or interested in off grid living, this comparison will provide you with valuable insights. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of which soil type is better suited for your gardening needs. So, let’s dive in and discover the pros and cons of raised bed soil and potting soil.
Comparison: Raised Bed Soil vs Potting Soil

Introduction
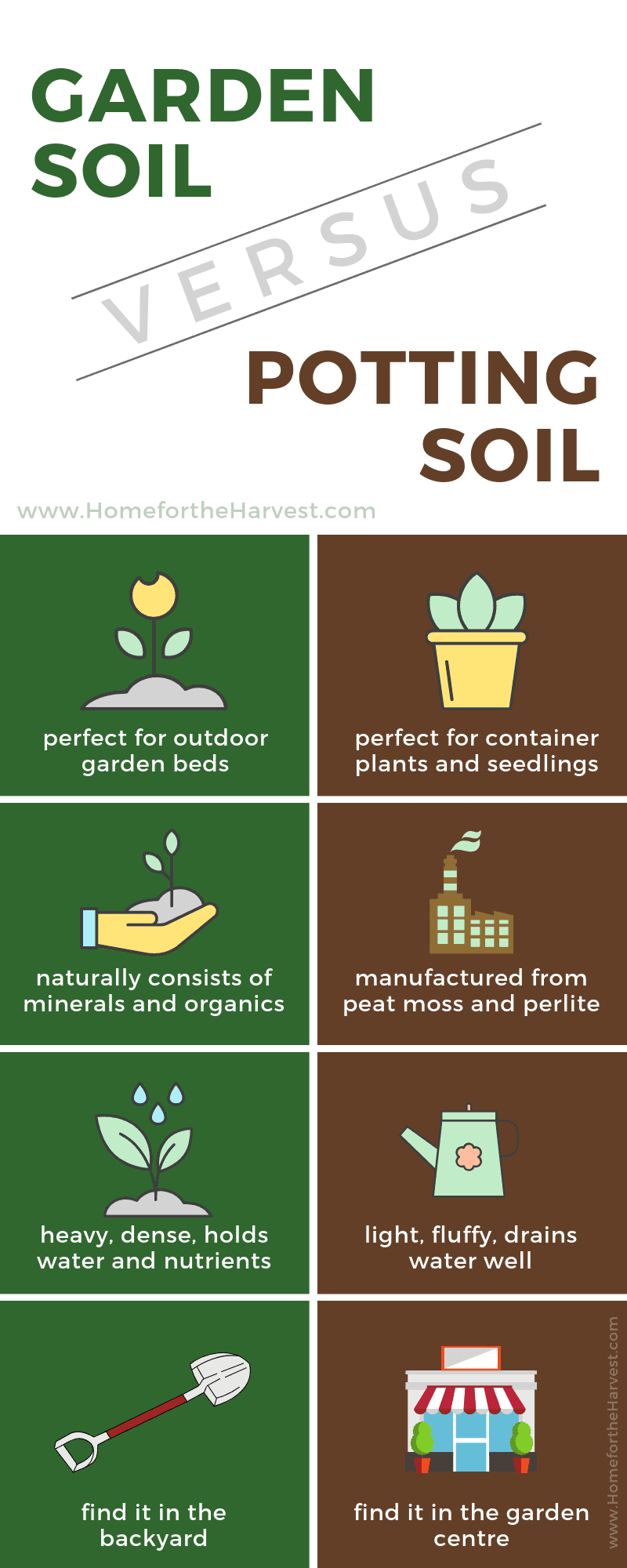
When it comes to gardening, choosing the right soil is crucial for the success of your plants. Two popular options for gardeners are raised bed soil and potting soil. Each type of soil has its own unique qualities and benefits, making the decision of which to use a critical one. In this article, we will explore the differences between raised bed soil and potting soil, and discuss their advantages and disadvantages. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of which soil is most suitable for your gardening needs.
Understanding Raised Bed Soil
What is raised bed soil?
Raised bed soil, as the name suggests, is specifically designed for raised bed gardening. Raised beds are elevated containers filled with soil, providing a controlled environment for plants to thrive. Raised bed soil is a specially formulated blend that is tailored to meet the specific needs of plants grown in raised beds.
Composition of raised bed soil
Raised bed soil typically consists of a mixture of sandy loam, compost, and other organic materials. The combination of these ingredients ensures good drainage, aeration, and nutrient availability for plants. The soil is usually light and loose, allowing plant roots to penetrate easily and access water and nutrients.
Benefits of using raised bed soil
There are several benefits to using raised bed soil. Firstly, the loose and friable texture promotes healthy root growth and reduces the risk of compaction. This allows plants to absorb water and nutrients more efficiently. Additionally, raised bed soil provides excellent drainage, preventing excess water buildup and reducing the risk of root rot. Finally, the composition of raised bed soil is rich in organic matter, which improves soil fertility and encourages beneficial microbial activity.
Exploring Potting Soil
What is potting soil?
Potting soil is a type of soil specifically designed for container gardening. Unlike raised bed soil, which is designed for raised beds, potting soil is suitable for a wide range of containers, such as pots, hanging baskets, and window boxes. Potting soil provides an ideal growing medium for plants in containers, allowing them to thrive in a confined space.
Composition of potting soil
Potting soil is a blend of various organic and inorganic materials. It typically consists of a mixture of peat moss, perlite, vermiculite, and other organic matter. These components provide good aeration and moisture retention, ensuring that plant roots have access to both air and water.
Advantages of using potting soil
Potting soil offers several advantages for container gardening. Firstly, it provides excellent drainage, preventing water from pooling at the bottom of the container and potentially drowning the plant’s roots. Additionally, potting soil retains moisture well, ensuring that plants have a constant supply of water. The rich organic matter in potting soil also helps to foster beneficial microbial activity, promoting healthy root development and nutrient uptake.
Differences Between Raised Bed Soil and Potting Soil
Now that we have explored the characteristics of raised bed soil and potting soil individually, let us compare their differences.
Drainage capabilities
Raised bed soil and potting soil differ in their drainage capabilities. Raised bed soil is designed to provide good drainage, preventing excess water buildup and reducing the risk of root rot. On the other hand, potting soil is formulated to retain moisture, allowing plants in containers to access water for a longer duration between waterings.
Nutrient content
The nutrient content of raised bed soil and potting soil can vary. Raised bed soil often contains a higher level of nutrients, as it is designed for plants that have larger root systems and require more nutrients. Potting soil, while still containing essential nutrients, may have a lower nutrient content due to the smaller root systems of container plants.
Water retention
Raised bed soil and potting soil also differ in their water retention capabilities. Raised bed soil is typically designed to drain well, allowing excess water to escape and preventing waterlogging. This is beneficial for plants that are susceptible to root rot. Potting soil, on the other hand, retains moisture more effectively, ensuring plants in containers have a constant supply of water.
Suitability for different plants
The choice between raised bed soil and potting soil depends on the type of plants you intend to grow. Raised bed soil is suitable for a wide range of plants, including vegetables, herbs, and flowers that are planted in raised beds. Potting soil, on the other hand, is versatile and can be used for a variety of container plants, both indoors and outdoors.

Pros and Cons of Raised Bed Soil
Advantages of raised bed soil
- Promotes healthy root growth: The loose and friable texture of raised bed soil allows plant roots to penetrate easily and access water and nutrients efficiently.
- Good drainage: Raised bed soil provides excellent drainage, preventing water buildup and reducing the risk of root rot.
- Rich in organic matter: Raised bed soil is typically rich in organic matter, improving soil fertility and promoting beneficial microbial activity.
Disadvantages of raised bed soil
- Cost: Raised bed soil can be more expensive than other types of soil due to its specialized formulation.
- Weight: Raised bed soil can be heavy, especially when filling larger raised beds, making them difficult to move or transport.
Pros and Cons of Potting Soil
Advantages of potting soil
- Excellent drainage: Potting soil provides excellent drainage, preventing waterlogging and ensuring healthy root growth.
- Moisture retention: Potting soil retains moisture well, ensuring that plants have a constant supply of water.
- Versatility: Potting soil can be used for a wide range of container plants, both indoors and outdoors.
Disadvantages of potting soil
- Limited nutrient content: Potting soil may have a lower nutrient content compared to raised bed soil, as it is designed for smaller container plants.
- Cost: Depending on the brand and quality, potting soil can be relatively more expensive compared to other types of soil.

Choosing the Right Soil for Container Gardening
When it comes to choosing the right soil for container gardening, there are several factors to consider.
Factors to consider
- Drainage: Evaluate the drainage requirements of the plants you intend to grow and choose a soil that meets those requirements.
- Water retention: Consider the water needs of your plants and choose a soil that retains moisture adequately.
- Nutrient requirements: Different plants have different nutrient needs, so choose a soil that provides the appropriate nutrient content.
- Container size and weight: Consider the size and weight of your containers, as heavier soils can be challenging to move or transport.
Preference for specific plants
Certain plants have specific soil requirements. Research the optimal soil conditions for the plants you wish to grow and select the soil accordingly.
Container size and weight
The size and weight of your containers will determine the type of soil you choose. Lighter potting soil is more suitable for hanging baskets and smaller pots, while heavier raised bed soil is better for large raised beds.
Application of Raised Bed Soil
Where to use raised bed soil
Raised bed soil is specifically designed for raised beds, making it ideal for growing vegetables, herbs, flowers, and other plants in this type of gardening setup. Raised beds are particularly beneficial for urban gardens, rooftop gardens, and areas with poor soil quality.
Best practices for using raised bed soil
To ensure the best results when using raised bed soil, follow these tips:
- Fill raised beds to the recommended depth, typically around 8-12 inches.
- Regularly monitor moisture levels to prevent overwatering or dehydration.
- Supplement the soil with organic matter or compost to maintain soil fertility.
- Rotate crops to prevent nutrient depletion and pest infestations.
- Practice proper weed control to prevent competition for nutrients and water.

Application of Potting Soil
Where to use potting soil
Potting soil is versatile and can be used in various containers, both indoors and outdoors. It is suitable for potted plants, hanging baskets, window boxes, and other container gardening setups.
Best practices for using potting soil
To optimize plant growth when using potting soil, consider the following guidelines:
- Select containers with proper drainage holes to prevent waterlogging.
- Ensure containers are adequately sized to accommodate plant roots.
- Water plants thoroughly, allowing excess water to drain out of the containers.
- Fertilize plants regularly with appropriate nutrients, as potting soil may have a lower nutrient content.
- Monitor moisture levels closely, as potting soil can dry out quickly in smaller containers.
Comparing Costs
Cost analysis of raised bed soil
The cost of raised bed soil can vary depending on factors such as brand, quality, and quantity. While raised bed soil may be more expensive compared to regular garden soil, its specialized formulation and benefits make it a worthwhile investment for raised bed gardening.
Cost analysis of potting soil
Similar to raised bed soil, the cost of potting soil can vary based on brand, quality, and quantity. Potting soil may be relatively more expensive compared to regular garden soil due to its specialized formulation for container plants.

Environmental Impact
Sustainability of raised bed soil
The sustainability of raised bed soil depends on the sourcing of its components and the practices used in its production. Look for raised bed soil brands that prioritize sustainable sourcing and production methods, such as using organic materials and promoting responsible production.
Sustainability of potting soil
The sustainability of potting soil also relies on responsible sourcing and production practices. Look for potting soil brands that prioritize sustainable materials and production methods, as well as options that use renewable resources and minimize environmental impact.
Real-life Experiences
Testimonials of using raised bed soil
Many gardeners who have used raised bed soil have reported successful results. They appreciate the improved drainage, nutrient availability, and ease of root growth that raised bed soil provides. Some gardeners have even seen higher yields and healthier plants compared to traditional in-ground gardening.
Testimonials of using potting soil
Gardeners who have utilized potting soil for their container plants have also shared positive experiences. They praise the excellent drainage, moisture retention, and overall health of their plants when using potting soil. The versatility and convenience of potting soil have also been appreciated by both beginner and experienced gardeners.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing the right soil is crucial for the success of your gardening endeavors, whether you opt for raised bed soil or potting soil. Raised bed soil is ideal for raised bed gardening, offering benefits such as improved drainage, nutrient availability, and root growth. On the other hand, potting soil is versatile and suitable for a wide range of container plants, providing excellent drainage and moisture retention. Consider the specific needs of your plants, the type of gardening setup, and your own preferences when making a decision. Regardless of the soil you choose, with proper care and attention, your plants will thrive and reward you with beautiful blooms or bountiful harvests. Happy gardening!
Note: This article is based on general knowledge and experience in gardening and does not take into account specific individual circumstances. Always conduct your own research and consult with experts for personalized advice.