Hello there! In this article, we’ll be discussing compost-based gardening in raised beds. We’ll provide some useful information about off-grid living and how it ties into gardening. Additionally, we’ll answer the question of whether you can use compost alone in a raised bed. So, if you’re interested in learning more about sustainable gardening practices and maximizing your composting efforts, keep reading!
Compost-based Gardening in Raised Beds

Introduction to Compost-based Gardening in Raised Beds
Compost-based gardening in raised beds is a sustainable and efficient approach to growing plants. By utilizing the power of compost, you can create nutrient-rich soil that promotes healthy plant growth. In this article, we will explore the concept of raised beds in gardening, the benefits of using compost, and the possibilities of compost-only gardening.
Understanding the concept of raised beds in gardening
Raised beds in gardening refer to elevated planting areas that are built above the ground level. These beds are usually 6-12 inches high and can be made from a variety of materials such as wood, stone, or metal. The raised bed structure provides several advantages for gardeners, including improved drainage, better soil retention, and easier access for planting and harvesting.
The benefits of using compost in raised beds
Using compost in raised beds offers numerous benefits to your plants and the environment. Compost is a rich source of organic matter and essential nutrients that nourish the soil and promote healthy plant growth. It enhances soil structure, improves water retention, and encourages beneficial microbial activity. Additionally, composting helps reduce waste and supports a more sustainable approach to gardening.
Exploring the possibilities of compost-only gardening
Compost-only gardening is an exciting concept that involves growing plants solely in compost-filled raised beds. With this approach, you can eliminate the need for traditional soil and rely solely on nutrient-rich compost to support plant growth. Compost-only gardening offers a unique opportunity to create a controlled environment that maximizes the benefits of compost for your plants.
Choosing the Right Compost for Raised Beds
To make the most of your compost-based gardening in raised beds, it is crucial to choose the right type of compost. Different compost options are available, each with its own unique properties. Let’s explore the different types of compost and compare organic and synthetic options.
Different types of compost available
When selecting compost for raised beds, you can choose between homemade compost or commercially available compost. Homemade compost is created by decomposing organic matter such as food scraps, yard waste, and plant residues. On the other hand, commercially available compost is typically made from a combination of organic and synthetic materials.
Comparing organic and synthetic compost options
Organic compost is derived from natural sources and is free from any artificial additives or chemicals. It is rich in nutrients and microbial activity, making it ideal for promoting healthy soil and plant growth. Synthetic compost, also known as manufactured or bagged compost, is formulated using synthetic materials and may contain added chemicals and fertilizers. While it can provide quick results, synthetic compost may lack the long-term benefits of organic compost.
Factors to consider when selecting compost for raised beds
When choosing compost for your raised beds, it is important to consider several factors. Firstly, assess the nutrient content of the compost and ensure it aligns with the specific needs of your plants. Additionally, consider the pH level of the compost to ensure compatibility with the types of plants you intend to grow. Lastly, evaluate the texture and overall quality of the compost, as this will affect its ability to retain moisture and support root development.
Preparing and Building Raised Bed Structures
To start your compost-based gardening journey, you will need to prepare and build the raised bed structures. Let’s go through the steps involved in determining the ideal size, gathering the necessary materials, and constructing the raised beds.

Determining the ideal size and dimensions of raised beds
The size and dimensions of raised beds depend on various factors, including the available space, the types of plants you wish to grow, and your personal preferences. In general, raised beds should be around 4 feet wide to allow for easy access from both sides. The length can vary depending on the available space, but it is best to keep it under 12 feet to prevent compaction in the center.
Materials required for building raised beds
You have several options when it comes to choosing materials for building raised beds. Some popular choices include using untreated wood, concrete blocks, or even repurposed materials such as old bathtubs or wine barrels. It is important to select materials that are sturdy, durable, and safe for use in a garden setting.
Step-by-step instructions for constructing raised beds
Building raised beds is a straightforward process that can be completed with basic tools and materials. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you construct your own raised beds:
- Measure and mark the desired dimensions of your raised beds on the ground.
- Use a shovel or garden rake to remove any existing vegetation and debris from the designated area.
- Lay out the materials for the raised bed, ensuring they are aligned properly.
- Secure the corners of the raised bed by either using connectors or driving stakes into the ground.
- Fill the raised bed with compost, leaving a small gap at the top for watering and plant growth.
- Smooth out the surface of the compost, ensuring it is evenly distributed.
- Water the compost lightly to encourage settling.
Optimal Placement and Location of Raised Beds
The placement and location of your raised beds play a crucial role in determining the success of your compost-based gardening. Consider factors such as sunlight, shade requirements, and maximizing space and accessibility.
Considering sunlight and shade requirements
Before placing your raised beds, it is important to assess the sunlight and shade patterns in your garden. Most vegetables and fruits require at least six hours of direct sunlight each day. Therefore, choose a location that receives adequate sunlight while also considering any existing shade-producing structures such as trees or buildings.
Factors to consider when choosing the placement of raised beds
When placing your raised beds, take into account the ease of access and the overall aesthetics of your garden. Ensure there is enough space between each bed for you to comfortably maneuver while tending to your plants. Consider the proximity to water sources for convenient watering and ensure the raised beds are not at risk of being damaged by water runoff.
Tips for maximizing space and accessibility
To make the most of your gardening space, consider utilizing vertical gardening techniques. Install trellises or stakes to support vining plants such as tomatoes or cucumbers, allowing them to grow vertically instead of sprawling across the ground. This not only maximizes space but also improves air circulation and reduces the risk of disease.
Preparing the Soil for Compost-based Gardening
Once your raised beds are in place, it is time to prepare the soil for compost-based gardening. This involves clearing existing vegetation and debris, loosening and conditioning the soil, and incorporating compost to enhance its fertility.
Clearing existing vegetation and debris
Before incorporating compost into the soil, remove any existing vegetation and debris from the raised beds. This helps prevent weed growth and provides a clean slate for your plants to thrive. Use a garden rake or hand tools to remove the unwanted materials, ensuring you get rid of all the roots and weeds.

Loosening and conditioning the soil for improved drainage
To improve the drainage and overall structure of the soil, it is important to loosen and condition it. Use a garden fork or a tiller to break up any compacted soil and remove large clumps. This allows for better water penetration and root growth.
Methods for incorporating compost into the existing soil
Incorporating compost is essential for enriching the soil with organic matter and nutrients. There are several methods to achieve this, such as mixing the compost into the soil using a garden fork or shovel, or by layering the compost on top of the soil and allowing it to naturally integrate over time. Choose the method that best suits your gardening preferences and the needs of your plants.
Layering and Maintaining Compost in Raised Beds
After preparing the soil, it is time to focus on layering and maintaining compost in your raised beds. This ensures a balanced combination of nutrients and organic matter, promoting a healthy and productive garden environment.
Understanding the concept of compost layering
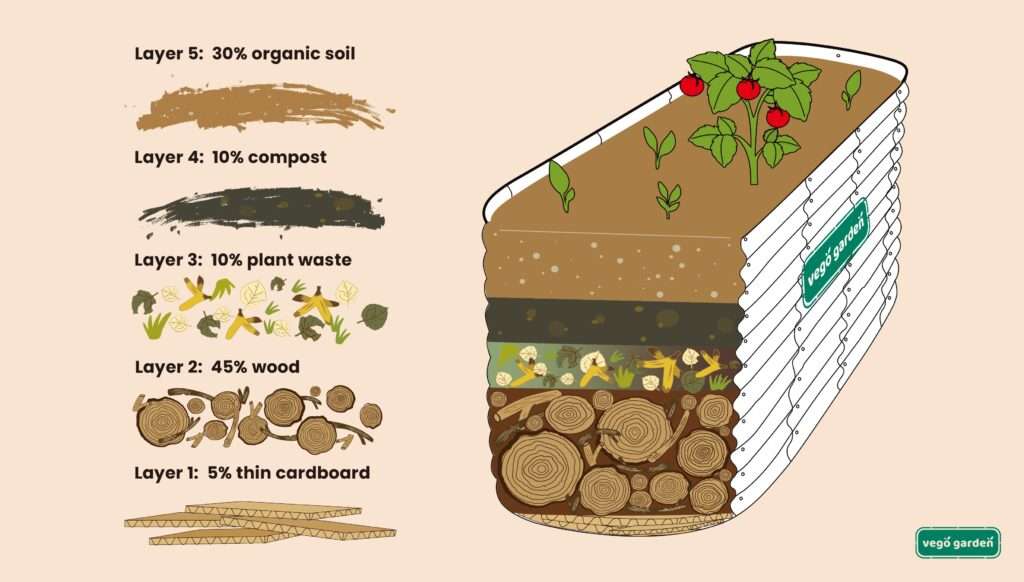
Compost layering, also known as lasagna gardening, involves creating alternating layers of compost and other organic materials within the raised bed. This method encourages decomposition and helps to create a nutrient-rich soil environment for your plants. Begin by laying down a layer of cardboard or newspaper to prevent weeds from growing, followed by alternating layers of compost, grass clippings, leaves, and other organic matter.
Tips for achieving the right balance of nutrients and organic matter
To achieve the right balance of nutrients and organic matter in your raised beds, consider both the quantity and quality of the compost you use. Aim for a compost-to-soil ratio of 1:4 or 1:3, depending on the needs of your plants. Regularly monitor the moisture level of the compost and adjust watering accordingly to maintain optimal conditions for decomposition.
Maintenance practices to keep the compost healthy and productive
To keep your compost healthy and productive, regular maintenance is required. Turn the compost pile periodically to promote even decomposition and improve aeration. Additionally, monitor the moisture levels and adjust as necessary. Avoid compacting the compost and ensure proper drainage to prevent waterlogging.
Selecting Suitable Plants for Compost-based Gardening
To thrive in a compost-based gardening environment, it is important to select the right plants. Different vegetables and fruits have varying nutrient requirements, and some plants are better suited for the nutrient-rich soil provided by compost.
Choosing vegetables and fruits that thrive in compost-rich soil
Many vegetables and fruits thrive in compost-rich soil due to the abundance of nutrients and organic matter. Leafy greens such as lettuce, spinach, and kale are excellent choices, as they benefit from the increased nutrient availability. Other suitable plants include tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, beans, and herbs such as basil or parsley. Consider the specific growing requirements of each plant to ensure success.
Considering the specific nutrient requirements of different plants
Different plants have varying nutrient requirements, so it is important to consider these when selecting plants for your compost-based raised beds. Pay attention to the specific macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium) needed for each plant, as well as micronutrients such as calcium, magnesium, and iron. This knowledge will help you create an optimal growing environment for your plants.
Companion planting in compost-based raised beds
Companion planting involves growing certain plants together to maximize their growth potential and deter pests. In compost-based raised beds, companion planting can further enhance the overall gardening experience. For example, planting marigolds alongside tomatoes can help deter pests, while growing carrots and onions together can repel specific insects. Research and experiment with companion planting to discover beneficial plant combinations.
Watering and Irrigation Techniques for Raised Beds
Proper watering and irrigation techniques are essential for the health and productivity of your compost-based raised beds. Understanding the water requirements of compost-based gardening, choosing the right irrigation system, and implementing effective watering practices will ensure your plants thrive.
Understanding the water requirements of compost-based gardening
Compost-based gardening typically requires a consistent level of moisture to support plant growth. While compost retains moisture well, it is important to balance this with good drainage to prevent waterlogging. Take into account the specific water requirements of your plants and monitor the moisture levels regularly.
Choosing the right irrigation system for raised beds
Several irrigation systems are suitable for raised beds, including soaker hoses, drip irrigation, or hand watering. Soaker hoses and drip irrigation systems are particularly effective as they deliver water directly to the base of the plants, minimizing evaporation and water waste. Experiment with different systems to find the one that best meets your needs and the needs of your plants.
Tips for efficient watering and moisture retention
To ensure efficient watering and moisture retention in your raised beds, there are several techniques you can implement. Mulching the soil surface with organic materials such as straw or wood chips helps retain moisture and reduce evaporation. Water deeply and less frequently to encourage deep root growth, and water in the early morning or late afternoon to minimize water loss due to evaporation.
Weed Control and Pest Management in Compost-based Gardening
Weed control and pest management are essential aspects of compost-based gardening. Implementing natural weed control methods, identifying and preventing common pests, and practicing integrated pest management techniques will help maintain a healthy and productive garden.
Natural weed control methods suitable for compost-based gardening
Weeds can compete with your plants for nutrients and water, so it is important to control them effectively. Some natural weed control methods suitable for compost-based gardening include using mulch or landscape fabric to smother the weeds, manually pulling them out, or using vinegar-based herbicides. It is important to stay vigilant and tackle weeds as soon as they appear to prevent them from spreading.
Identifying and preventing common pests in raised beds
Common pests in raised beds include aphids, slugs, snails, and caterpillars. Research and identify the pests specific to your region and the plants you are growing. Implement preventative measures such as regularly inspecting your plants, using physical barriers, or introducing beneficial insects that prey on garden pests. In severe cases, consider organic pest control options such as neem oil or insecticidal soaps.
Integrated pest management practices
Integrated pest management (IPM) involves a comprehensive approach to pest control that emphasizes prevention and minimizes the use of chemical treatments. IPM practices include monitoring and identifying pests, maintaining healthy soil and plants, introducing beneficial insects, and only resorting to organic or chemical treatments when necessary. By implementing IPM techniques, you can prevent and manage pest issues effectively.

Harvesting and Sustaining Compost-based Raised Beds
Knowing when and how to harvest your crops and sustain the long-term productivity of your compost-based raised beds is essential. By implementing proper harvesting techniques and following specific maintenance steps, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest and ensure the continued success of your garden.
Signs that indicate the readiness of plants for harvest
Different crops have varying signs that indicate they are ready for harvest. For vegetables, such as lettuce or radishes, you can harvest when they have reached the desired size or maturity. For fruits, such as tomatoes or peppers, harvest when they have developed the appropriate color and texture. Regularly monitor your plants and research the specific harvesting indicators for each crop.
Proper harvesting techniques for different crops
To ensure the quality and longevity of your crops, it is important to use proper harvesting techniques. Use pruning shears or garden knives to harvest vegetables or herbs, ensuring a clean cut without damaging the plants. For fruits, carefully twist or cut them from the vine, taking care not to bruise or damage the surrounding plant.
Steps to maintain the long-term productivity of raised beds
To sustain the long-term productivity of your raised beds, regular maintenance is required. After each harvest, remove any plant debris and incorporate it into the compost pile. Conduct soil tests periodically to assess nutrient levels and adjust compost additions accordingly. Rotate your crops each season to prevent the buildup of pests and diseases, and regularly monitor for signs of nutrient deficiencies or other issues.
Alternative Approaches to Compost-based Raised Bed Gardening
While compost-based gardening in raised beds is a popular and effective approach, there are alternative methods to explore. No-dig and lasagna gardening techniques offer unique benefits, while vertical gardening allows you to maximize limited space in a compost-based growing environment.
Exploring no-dig and lasagna gardening methods
No-dig gardening, also known as sheet mulching or lasagna gardening, involves creating layers of organic materials directly on top of the soil, eliminating the need for deep digging. This technique mimics the natural decomposition process and promotes a healthy soil environment. By layering materials such as compost, straw, leaves, and cardboard, you can create rich, nutrient-dense soil for your plants.
Innovative techniques for composting in limited spaces
Composting in limited spaces can be challenging, but there are innovative techniques to overcome this constraint. Vermicomposting, also known as worm composting, utilizes worms to break down organic matter, producing nutrient-rich castings. Bokashi composting is another option, which involves fermenting organic waste in an airtight container. These methods offer compact and efficient ways to compost, allowing you to incorporate compost into your raised beds even in limited spaces.
Vertical gardening in compost-based raised beds
Vertical gardening is a technique that involves growing plants vertically, using trellises or structures to support their growth. In compost-based raised beds, vertical gardening allows you to maximize the available space and increase your plant yield. Vining plants such as tomatoes, cucumbers, or beans can be trained to grow vertically, reducing the footprint in the raised beds and creating a visually appealing garden.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Compost-based Gardening
While compost-based gardening in raised beds offers numerous benefits, certain issues may arise. By identifying nutrient deficiencies, addressing excessive moisture or drainage problems, and preventing and managing disease outbreaks, you can overcome common challenges.
Identifying nutrient deficiencies and addressing them
Nutrient deficiencies can manifest in various ways, such as stunted growth, discoloration, or yellowing of leaves. Conduct soil tests to identify any deficiencies and then supplement the soil with the necessary nutrients. This can be done through the addition of well-balanced compost or specific organic fertilizers, depending on the deficiency.
Dealing with excessive moisture or drainage problems
Excessive moisture or poor drainage in raised beds can lead to waterlogging, root rot, and other detrimental conditions for your plants. To address this issue, ensure your raised beds have proper drainage systems in place. Consider incorporating drainage rocks or gravel at the bottom of the beds and adjusting the soil composition to improve drainage. Regularly monitor soil moisture levels and adjust watering practices as necessary.
Preventing and managing disease outbreaks in raised beds
Disease outbreaks can impact the health and productivity of your compost-based raised beds. To prevent and manage diseases, practice proper sanitation by removing any diseased plant material promptly. Rotate your crops each season to minimize the buildup of disease-causing pathogens. Implement preventative measures, such as spacing plants appropriately to encourage airflow and reduce humidity. Consider using disease-resistant varieties and organic sprays or treatments when necessary.
Exploring the Sustainability of Compost-based Gardening
Compost-based gardening in raised beds offers numerous environmental benefits, contributing to a healthier ecosystem, reducing waste, and promoting biodiversity and soil health.
Environmental benefits of composting and raised bed gardening
Composting and raised bed gardening provide several environmental benefits. Composting helps divert organic waste from landfills, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and minimizing landfill space. Raised bed gardening reduces the need for tilling and traditional soil, preserving the natural structure of the ground. Furthermore, both practices promote healthy soil, which in turn supports diverse plant and animal life.
Reducing waste and contributing to a healthier ecosystem
By composting organic waste and using it in raised beds, you can significantly reduce waste. Food scraps, yard waste, and other organic materials can be diverted from the landfill, reducing methane gas emissions and contributing to a healthier ecosystem. Compost-based gardening also reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, minimizing the harmful impact on the environment.
Promoting biodiversity and soil health through compost-based gardening
Compost-based gardening fosters biodiversity and soil health by creating a nutrient-rich environment. The diverse organic matter in compost supports a wide range of soil organisms, from earthworms to beneficial microbes, enhancing the overall soil ecosystem. This, in turn, promotes plant health and resilience, reduces the risk of pests and diseases, and ensures long-term productivity.
Conclusion
Compost-based gardening in raised beds offers a sustainable and rewarding approach to growing plants. By understanding the concept of raised beds, utilizing the benefits of compost, and implementing proper gardening practices, you can create a thriving garden environment. From choosing the right compost to sustaining long-term productivity, this article has provided you with comprehensive insights and tips to enhance your compost-based gardening journey. Embrace this sustainable gardening approach, explore the possibilities, and enjoy the countless rewards of compost-based gardening in your raised beds.




