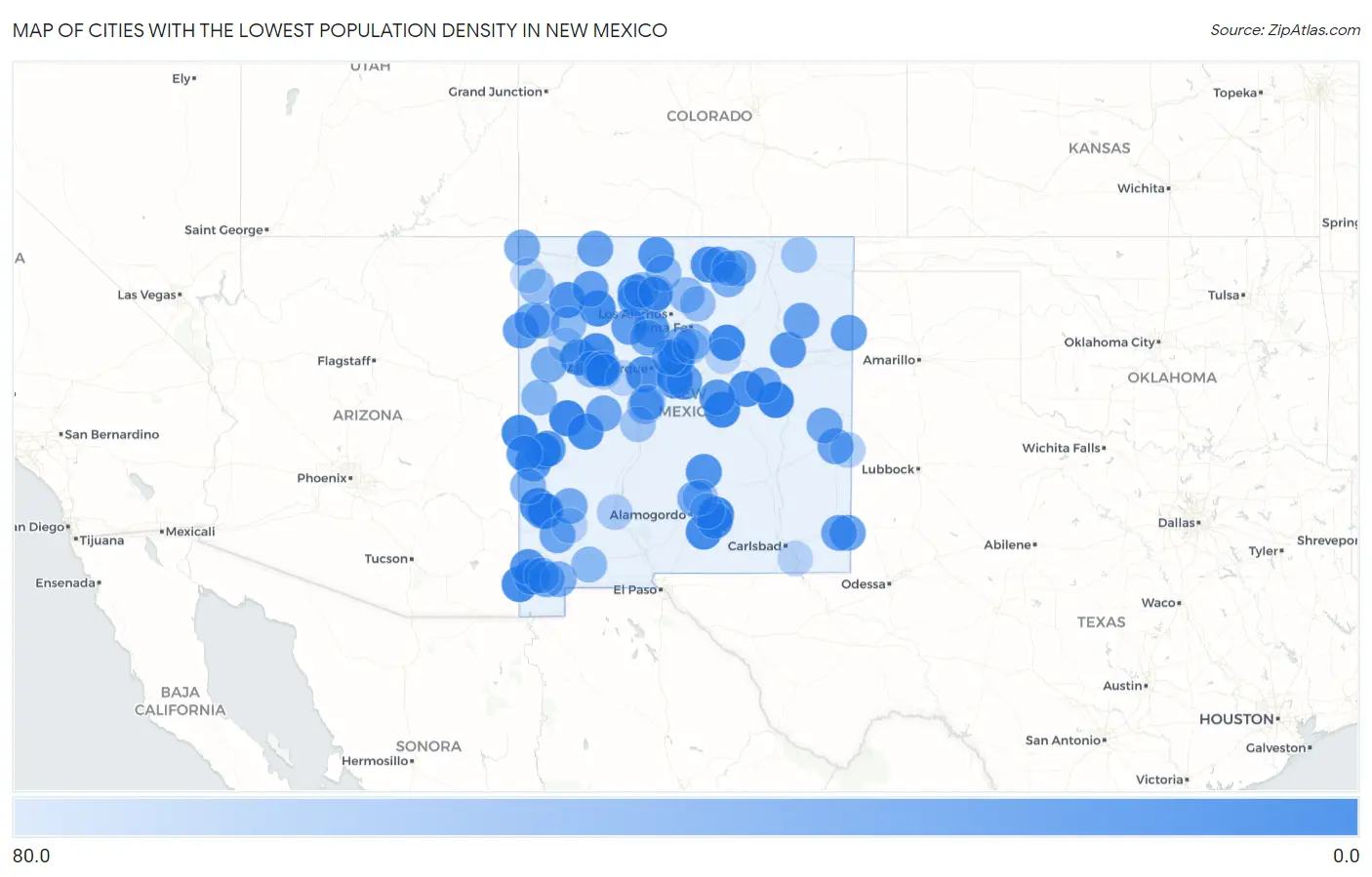
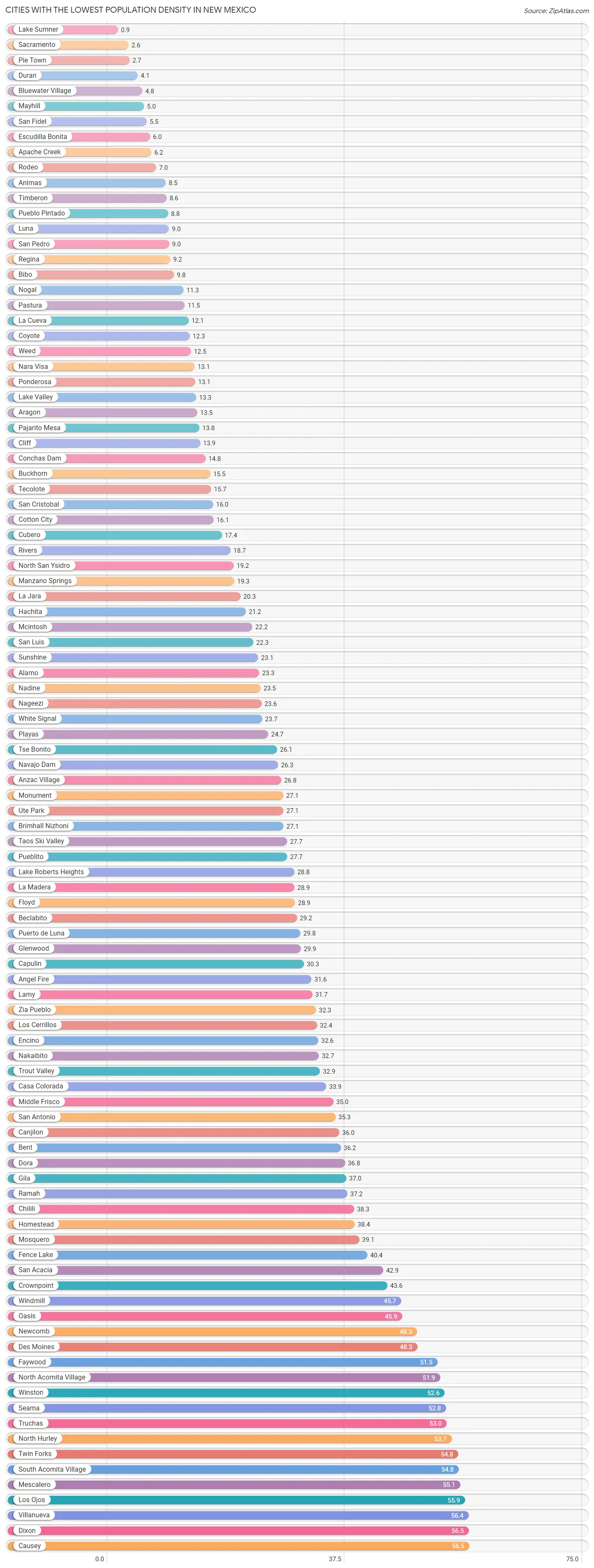
New Mexico’s low population density in the southern United States makes it an attractive destination for those seeking solitude and tranquility. With only two cities boasting a population over 100k, Albuquerque and Las Cruces, the vast expanses of this semi-arid region are sparsely inhabited, offering a sense of seclusion not easily found elsewhere. However, this remote living comes with its own set of challenges. Freshwater scarcity and high crime rates necessitate careful planning for those looking to embrace off-grid living. Additionally, the arid climate and low fertility of the land make growing crops a difficult endeavor. Despite these obstacles, the cost of housing and land in New Mexico is remarkably affordable, with a property tax rate well below the national average. While the cost of living may be below average, the state’s higher unemployment rate and above-average crime rate should be taken into consideration. As with any location, New Mexico is susceptible to natural disasters, including storms, floods, heatwaves, and occasional tornadoes. So, whether you are enticed by the allure of living off the grid in a remote desert landscape or simply curious about the unique characteristics of this southern state, New Mexico’s low population density is sure to captivate the adventurous soul.
Geographic Location and Population Density
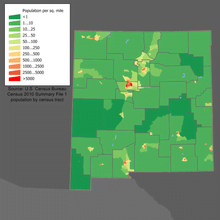
New Mexico is located in the southern part of the United States, bordered by Texas to the east, Arizona to the west, Colorado to the north, and Mexico to the south. Despite its large land area of approximately 121,590 square miles, New Mexico has a relatively low population density.
What is population density?
Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area. It is calculated by dividing the total population of an area by its land area. In the case of New Mexico, its low population density means that there are fewer people per square mile compared to other states in the country.
Comparison of New Mexico’s population density with other states
When we compare New Mexico’s population density with other states in the U.S., it falls on the lower end of the spectrum. As of 2021, New Mexico has a population density of around 17.2 people per square mile. In contrast, states like New Jersey and Rhode Island have much higher population densities of 1,210 and 1,012 people per square mile, respectively.
The low population density in New Mexico can be attributed to various factors, such as its vast desert landscapes and limited access to water sources. These unique characteristics pose challenges for those looking to live off-grid in the state.
Challenges of Off-Grid Living in New Mexico
Living off-grid refers to the lifestyle of relying on self-sufficiency and renewable resources, rather than public utilities. In New Mexico, off-grid living is legal, but there are significant challenges that individuals or communities may face.
Legal status of off-grid living in New Mexico
New Mexico has relatively lenient regulations regarding off-grid living. The state allows individuals to build and live in structures without being connected to public utilities such as water, electricity, or sewer systems. This offers the opportunity for people to embrace a more sustainable and self-reliant way of life. However, it’s important to be aware of local zoning laws and building codes that may still apply.
Lack of fresh water for off-grid living
One of the primary challenges of off-grid living in New Mexico is the scarcity of fresh water. As a primarily desert state, New Mexico has limited water resources. Obtaining a reliable and sustainable source of water can be a significant obstacle for off-grid communities or individuals. Rainwater harvesting and well drilling are common methods used to address this challenge, but they require careful planning and investment.
High crime rates in rural areas
While New Mexico may offer the opportunity for secluded and peaceful off-grid living, it’s essential to consider safety concerns. The state has higher crime rates compared to the national average, particularly in rural areas. This can be attributed to a variety of factors, including drug trafficking routes, poverty, and limited law enforcement resources. It’s crucial to prioritize safety measures and community-building efforts to mitigate these risks.
Major Cities and Population Centers in New Mexico
New Mexico is home to several cities and population centers, but the two largest cities are Albuquerque and Las Cruces.
Albuquerque: The largest city in New Mexico
Albuquerque is the most populous city in New Mexico, with a population of over 560,000 residents. Situated in the central part of the state, Albuquerque serves as the economic and cultural hub of New Mexico. The city boasts diverse neighborhoods, a vibrant arts scene, and a rich history. It is also home to the University of New Mexico, providing educational opportunities and contributing to the city’s lively atmosphere.
Las Cruces: The second-largest city in New Mexico
Located in the southern part of the state, Las Cruces is the second-largest city in New Mexico, with a population of around 103,000 residents. Known for its scenic beauty and proximity to the Organ Mountains, Las Cruces offers a blend of small-town charm and modern amenities. The city’s economy is primarily driven by agriculture, education, and healthcare sectors. Las Cruces is also home to New Mexico State University, a prominent institution of higher learning.
Climate and Weather Patterns in New Mexico
New Mexico experiences a semi-arid climate, characterized by hot summers and mild winters. The state’s geographical features, such as its high elevation and mountain ranges, influence its weather patterns.
Semi-arid climate in New Mexico
The semi-arid climate of New Mexico means that the state receives relatively low annual precipitation. This can be challenging for those engaging in agriculture or off-grid living, as water scarcity poses significant obstacles. The dry climate also contributes to the risk of wildfires, particularly during periods of drought.
Hot summers and mild winters
Summers in New Mexico are typically hot, with temperatures often exceeding 90 degrees Fahrenheit. The intense heat can be uncomfortable for some individuals, requiring careful consideration of cooling methods and water conservation. On the other hand, winters in New Mexico are relatively mild, with average temperatures ranging from the 40s to the 60s. Snowfall occurs in certain parts of the state, particularly in higher elevations.
Agricultural Challenges and Land Fertility
Despite its agricultural potential, New Mexico presents challenges for farmers and gardeners due to various factors affecting land fertility.
Difficulty of growing crops in New Mexico
The arid and semi-arid climate of New Mexico, coupled with limited water resources, makes it challenging to grow crops successfully. Irrigation systems and crop rotation methods are crucial for maximizing water efficiency and soil health. Drought-resistant crops, such as chile peppers and pecans, are commonly cultivated in the region.
Low fertility of the land
Another obstacle to agriculture in New Mexico is the low fertility of the soil. Many areas consist of sandy or rocky soils with limited organic matter. This necessitates the use of soil amendments and fertilizers to improve fertility and increase crop yields. Additionally, farmers must carefully manage water usage and implement efficient irrigation systems to mitigate the effects of drought and limited water supply.
Diverse Wildlife of New Mexico
New Mexico is home to a diverse range of wildlife species, adapted to the arid and semi-arid ecosystems of the state.
Antelope: A common sight in New Mexico
Antelope, specifically the pronghorn, are a familiar sight in New Mexic