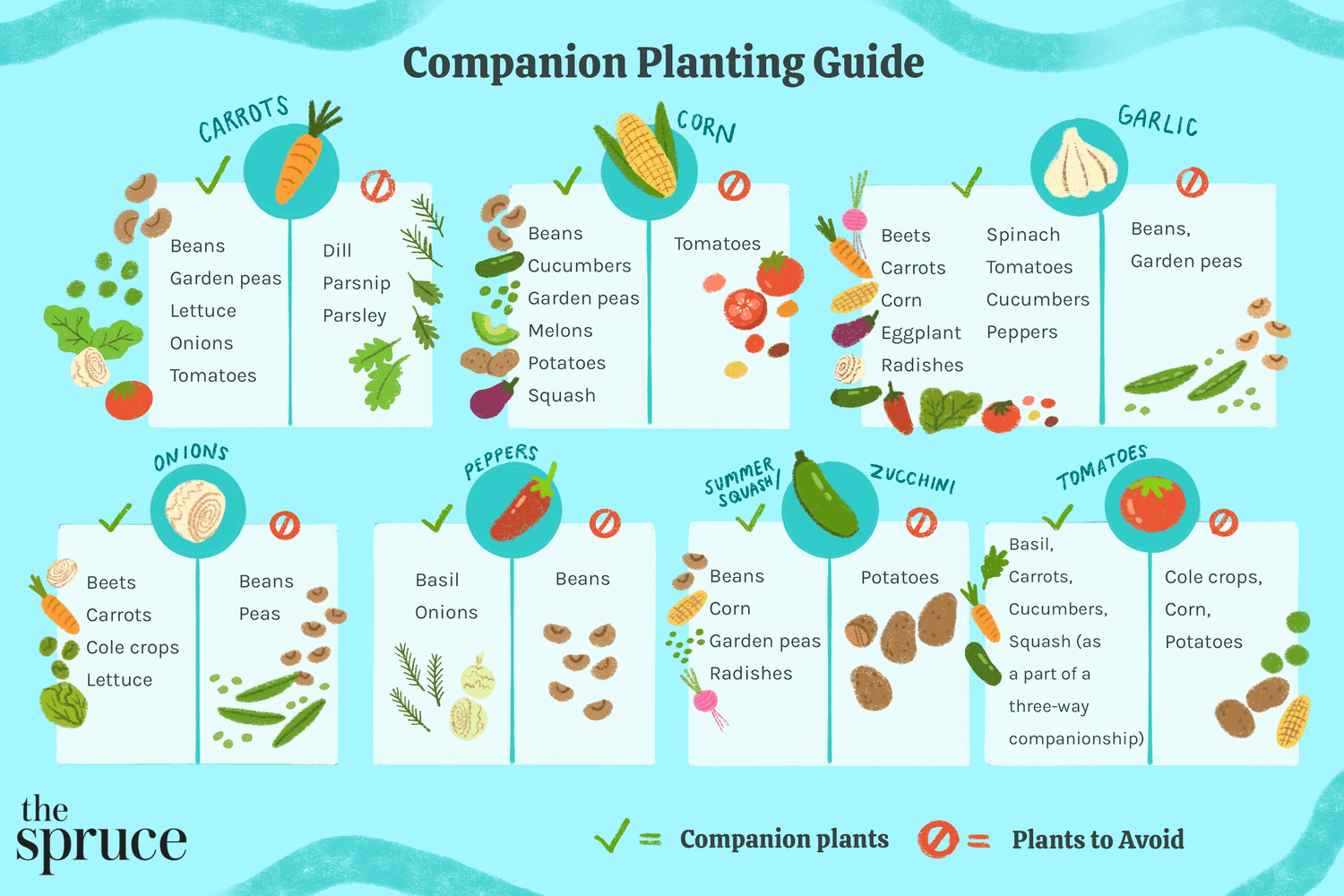
In this article, we will explore the concept of companion planting and how it can help maximize the yield of your vegetable garden. We will discuss the benefits of strategically pairing different plants together and what vegetables work best when planted alongside each other. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of how companion planting can enhance the health and productivity of your garden. So, let’s get started and discover the secrets of maximizing vegetable yield through strategic plant pairings!

Companion Planting: Maximizing Vegetable Yield with Strategic Plant Pairings
Companion planting is a gardening technique that involves growing different plants together in order to maximize vegetable yield and create a balanced ecosystem. By strategically pairing plants, gardeners can take advantage of their natural relationships to enhance growth, deter pests, and improve soil health. In this article, we will explore the benefits of companion planting, discuss various methodologies and techniques, and provide a comprehensive guide to help you make the most of this gardening method.
What is Companion Planting?
Companion planting is an ancient practice that has been used for centuries to create harmonious plant communities. It involves growing different plant species in close proximity to each other, based on the belief that certain plants have the ability to enhance the growth and overall health of their neighboring plants.
The concept behind companion planting revolves around the symbiotic relationships that exist in nature. Some plants emit chemical compounds that repel pests, while others attract beneficial insects for pest control or promote pollination. Companion planting also takes into consideration the nutritional needs of different plant species, maximizing their access to essential nutrients and sunlight.
Benefits of Companion Planting
Companion planting offers several benefits that can significantly improve the productivity and health of your vegetable garden. Some of the key advantages of companion planting include:
Pest control: Certain plants have natural pest-repellent properties, and by growing them alongside susceptible vegetables, you can deter common garden pests. This reduces the need for harmful pesticides and promotes a healthier, more sustainable garden ecosystem.
Increased yield: Companion planting can enhance the growth and productivity of vegetables by optimizing their nutrient intake and providing shade or support. By strategically pairing plants, you can create a harmonious environment that encourages higher yields and healthier crops.
Improved soil health: Different plants have varying nutrient requirements, and companion planting helps in creating a balanced nutrient cycle. Some plants can fix nitrogen in the soil, while others help with weed control or soil aeration. This holistic approach to gardening leads to improved soil fertility and overall plant health.
Pollination and fertility: Certain plants, such as flowers, attract pollinators like bees and butterflies. By incorporating these plants into your vegetable garden, you can increase pollination rates and ensure the successful reproduction of your crops. Similarly, companion planting can also encourage the growth of nitrogen-fixing plants, which enrich the soil with this essential nutrient.
Maximizing Vegetable Yield
Importance of Vegetable Yield
As a gardener, one of your primary goals is to maximize vegetable yield. Whether you are growing vegetables for personal consumption or for sale, a high yield ensures a bountiful harvest and a successful gardening season. Companion planting offers a holistic and sustainable approach to increasing vegetable yield by enhancing the overall health of plants and optimizing growing conditions.
Traditional Planting vs Companion Planting
In traditional planting methods, vegetables are often grown in monocultures, where a single plant species dominates a given space. While this method may seem convenient and organized, it has several drawbacks. Monocultures are highly susceptible to pests and diseases, as they provide a favorable environment for the rapid spread of such problems.
Companion planting, on the other hand, promotes biodiversity and creates a more resilient garden ecosystem. By diversifying your vegetable garden, you introduce beneficial species that support and protect each other. This decreases the likelihood of pest outbreaks and increases the overall health and productivity of your crops.

Strategic Plant Pairings
Understanding Plant Relationships
To effectively implement companion planting, it is important to understand the relationships between different plant species. Some plants have mutually beneficial relationships, while others may compete for resources or inhibit each other’s growth. By strategically selecting compatible plant pairings, you can create a harmonious garden that promotes growth and minimizes competition.
Choosing Plants for Pairings
When choosing plants for companion planting, consider factors such as their growth patterns, nutrient requirements, and pest-repellent properties. Some common companion planting strategies include:
Pest-repellent plants: Certain plants, such as marigolds, garlic, and basil, emit natural compounds that repel pests. Intercropping these plants with vulnerable vegetables can help protect them from common garden pests.
Beneficial insect attractors: Flowers like sunflowers, calendula, and alyssum attract beneficial insects like ladybugs and lacewings, which feed on garden pests. Planting these flowers near vegetables can promote a healthy garden ecosystem and natural pest control.
Nitrogen-fixing plants: Legumes, such as peas and beans, have the unique ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen into the soil. Intercropping these nitrogen-fixing plants with nitrogen-demanding vegetables, like tomatoes and corn, can improve soil fertility and enhance vegetable yield.
By considering these plant relationships and pairings, you can create a diverse and mutually beneficial garden that maximizes vegetable yield and promotes plant health.
Companion Planting Methodologies
Three Sisters Planting Method
The Three Sisters planting method is a traditional Native American companion planting technique that involves growing corn, beans, and squash together. These three crops have a symbiotic relationship, where each plant provides benefits to the others.
Corn provides a natural trellis for the beans to climb, while the beans fix nitrogen in the soil, benefiting the nitrogen-demanding corn. The squash acts as a living mulch, providing shade and suppressing weeds, which helps conserve soil moisture. This method maximizes space utilization, enhances soil fertility, and creates a balanced and sustainable garden ecosystem.
Trap Cropping
Trap cropping is a companion planting technique that involves planting attractive plants near susceptible vegetables to lure pests away from the main crop. The trap crops act as sacrificial plants, attracting pests away from the desired vegetables and providing a natural form of pest control.
For example, planting a row of radishes near cabbage can divert flea beetles’ attention away from the cabbage. This allows the cabbage to grow more safely while the trap crop absorbs most of the damage. Trap cropping is an effective strategy for minimizing pest damage without resorting to harmful pesticides.
Nurse Planting
Nurse planting involves growing a larger, more established plant near smaller or younger plants to provide them with shade, nutrients, or support. The nurse plants act as caretakers, protecting and nurturing the companion plants as they grow.
For instance, tall and sturdy sunflowers can serve as nurse plants for delicate and shallow-rooted lettuce seedlings. The sunflowers provide shade and support, preventing the lettuce from wilting or getting damaged by strong winds. Nurse planting facilitates the growth of weaker or vulnerable plants, ensuring their successful establishment in the garden.

Companion Planting Guide
Popular Vegetable Pairings
Companion planting offers a wide range of plant pairings that can enhance the growth and productivity of your vegetables. Here are some popular vegetable pairings that work well together:
Tomatoes and basil: Basil enhances the flavor of tomatoes and also repels pests like aphids and flies.
Carrots and onions: Onions deter carrot flies, while carrots can help to mask the onion scent, deterring onion pests.
Cucumbers and radishes: Radishes attract cucumber beetles away from cucumbers, protecting them from damage.
Beans and corn: Beans fix nitrogen in the soil, benefiting the nitrogen-demanding corn. The corn provides a natural trellis for the beans to climb.
By strategically pairing your vegetables, you can create a healthier and more productive garden.
Best Companion Plants for Tomatoes
Tomatoes are a popular vegetable in many gardens, and companion planting can help improve their growth and flavor. Some great companion plants for tomatoes include:
Basil: Basil enhances the flavor of tomatoes while also repelling pests like aphids and whiteflies.
Marigolds: Marigolds repel nematodes and deter pests like aphids and tomato hornworms.
Nasturtiums: Nasturtiums repel aphids, whiteflies, and other common tomato pests.
Borage: Borage attracts beneficial insects and repels tomato hornworms.
Planting these companion plants alongside your tomatoes can promote their growth while protecting them from common garden pests.
Ideal Herb and Vegetable Combinations
Pairing herbs with vegetables not only enhances the flavor of your dishes but can also benefit their growth. Here are some ideal herb and vegetable combinations:
Rosemary and cabbage: Rosemary repels cabbage moths and cabbage loopers, which are common pests for cabbage.
Dill and cucumbers: Dill attracts beneficial insects like wasps, which prey on cucumber beetles and other cucumber pests.
Sage and carrots: Sage deters pests like carrot flies, which can cause significant damage to carrot crops.
Thyme and tomatoes: Thyme has natural antifungal properties and can help prevent diseases like early blight in tomatoes.
By incorporating these herb and vegetable combinations into your garden, you can promote healthier plants and enhance the flavor of your harvest.
Companion Planting Techniques
Interplanting
Interplanting involves growing different plant species together in the same bed, allowing them to share resources and maximize space utilization. This technique is especially useful for small gardens or raised beds, where limited space requires strategic planting.
For example, interplanting lettuce, radishes, and carrots allows you to make efficient use of space while taking advantage of their different growing requirements. The lettuce provides shade and protects the more delicate radishes and carrots, while the radishes help break up the soil, benefiting the growth of the other two crops.
Interplanting allows you to grow a variety of crops and maximize the productivity of your garden bed.
Succession Planting
Succession planting is a technique that involves planting vegetables in multiple stages, allowing for a continuous harvest throughout the growing season. By staggering the planting dates, you ensure a steady supply of fresh produce and make the most of your garden space.
For example, if you have four rows for lettuce, you can plant one row every two weeks. As the first row is harvested, the second row will be ready to harvest, and so on. This extends the vegetable’s harvest period and prevents a glut or scarcity of produce at any given time.
Succession planting ensures a continuous and abundant supply of fresh vegetables from your garden throughout the growing season.
Vertical Gardening
Vertical gardening utilizes vertical space to maximize vegetable yield, especially in small gardens or limited spaces. By training plants to grow vertically using trellises, fences, or stakes, you can optimize space utilization and increase the number of plants you can grow.
Climbing vegetables like cucumbers, beans, and peas are excellent candidates for vertical gardening. By growing these plants upwards, you create more room for other crops while providing support and maximizing exposure to sunlight. Vertical gardening also improves air circulation, reducing the likelihood of disease and increasing overall plant health.

Organic Pest Control in Companion Planting
Natural Bug Repellent Strategies
Companion planting offers natural pest control solutions that reduce the need for harmful pesticides. By strategically pairing pest-repellent plants with susceptible vegetables, you can create a deterrent effect that keeps common garden pests at bay.
Some natural bug repellent strategies include:
Planting marigolds around susceptible vegetables to repel pests like aphids, nematodes, and whiteflies.
Interplanting garlic or onions with vulnerable vegetables to deter pests like carrot flies, aphids, and cabbage moths.
Growing strong-smelling herbs like basil, rosemary, and mint to mask the scent of vegetables and confuse pests.
These natural bug repellent strategies help protect your vegetables from pests while promoting an environmentally friendly gardening approach.
Beneficial Insects for Pest Control
Companion planting also encourages the presence of beneficial insects that act as predators or parasites to common garden pests. These beneficial insects help manage pest populations naturally, offering an alternative to chemical pest control methods.
Attracting beneficial insects to your garden can be achieved by incorporating nectar-rich flowers, such as alyssum, borage, and cosmos. These flowers attract pollinators like bees and butterflies, as well as predators like ladybugs and lacewings, which feed on garden pests. By creating a welcoming habitat for beneficial insects, you can establish a natural pest control system that supports healthy plant growth.
Herbs as Companion Plants
Using Herbs to Deter Pests
Many herbs have natural pest-repellent properties and can be used as effective companion plants to protect your vegetables from common garden pests. By interplanting herbs with susceptible vegetables, you can create a natural barrier that deters pests and reduces the need for harmful pesticides.
Some herbs commonly used for pest control in companion planting include:
Basil: Basil repels aphids, flies, and mosquitoes.
Mint: Mint deters ants, aphids, and cabbage moths.
Sage: Sage repels pests like cabbage moths, carrot flies, and slugs.
Rosemary: Rosemary deters pests like cabbage loopers and carrot flies.
By incorporating these herbs into your garden, you not only enhance the flavor of your harvest but also protect your vegetables from damaging pests.
Complementing Vegetable Flavors with Herbs
In addition to their pest-repellent properties, herbs also enhance the flavors of vegetables. Growing herbs alongside vegetables adds depth and complexity to your dishes, elevating the overall dining experience. Consider these herb and vegetable combinations:
Parsley and tomatoes: Parsley enhances the flavor of tomatoes and adds freshness to salads and sauces.
Cilantro and peppers: Cilantro complements the spicy flavor of peppers and is commonly used in salsas and Mexican cuisine.
Chives and potatoes: Chives add a mild onion-like flavor to potatoes, making them a popular pairing in savory dishes.
Oregano and zucchini: Oregano enhances the flavor of zucchini and is commonly used in Mediterranean-inspired dishes.
By incorporating herbs into your vegetable garden, you can create a diverse range of flavors and elevate your cooking to new heights.

Flowers in Companion Planting
Attracting Pollinators
Pollinators play a crucial role in fruit and vegetable production, and attracting them to your garden is essential for ensuring a successful harvest. Companion planting with flowers that attract pollinators can significantly increase pollination rates and enhance the productivity of your garden.
Some flowers that attract pollinators include:
Sunflowers: Sunflowers produce large, vibrant blooms that attract bees and other pollinators.
Calendula: Calendula flowers produce edible petals and attract bees and butterflies.
Alyssum: Alyssum is a low-growing flower that produces fragrant blooms, attracting bees and other beneficial insects.
By planting these flowers throughout your garden, you can attract pollinators and ensure optimal fruit and vegetable production.
Repelling Garden Pests with Flowers
Flowers can also be used to repel common garden pests and reduce the risk of damage to your vegetables. Some flowers have natural pest-repellent properties and can act as a deterrent to pests, reducing the need for harmful pesticides.
Here are some flowers that repel garden pests:
Marigolds: Marigolds repel nematodes and deter pests like aphids and whiteflies.
Nasturtiums: Nasturtiums repel aphids, whiteflies, and other common garden pests.
Chrysanthemums: Chrysanthemums contain a natural insecticide called pyrethrum, which repels a wide range of insects.
By incorporating these flowers into your garden beds, you can create a natural pest defense system that protects your vegetables and promotes a healthy garden ecosystem.
Companion Planting in Small Spaces
Container Gardening
Companion planting can be successfully applied to container gardening, making it a suitable method for small spaces such as balconies, patios, or windowsills. By carefully selecting compatible plant pairings and utilizing vertical space, you can maximize vegetable yield even in limited areas.
When choosing companion plants for container gardening, consider factors like their growth habit, root systems, and nutrient requirements. Some herbs and vegetables that thrive in containers and make good companion plants include tomatoes, basil, lettuce, and chives.
Ensure that your container provides adequate drainage, use quality potting soil, and water regularly to maintain healthy plants. Container gardening allows you to enjoy the benefits of companion planting, even in the smallest of spaces.
Vertical Gardening Techniques
Vertical gardening is another effective technique for maximizing vegetable yield in small spaces. By utilizing trellises, fences, or vertical planters, you can grow climbing vegetables and herbs, making efficient use of limited ground space.
Some vertical gardening techniques include:
Growing cucumbers, beans, or peas on trellises or arbors.
Utilizing hanging baskets or planters to grow trailing plants like tomatoes or strawberries.
Installing vertical planters on walls or fences for growing herbs or lettuce.
Vertical gardening not only saves space but also promotes better air circulation, sunlight exposure, and easier access to plants for maintenance and harvesting.
Companion Planting and Soil Health
Improving Soil Fertility
Soil health is crucial for the growth and productivity of your garden. Companion planting can contribute to soil fertility by utilizing plants with different nutrient requirements and incorporating nitrogen-fixing plants into your garden.
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plant growth, and nitrogen-fixing plants have the unique ability to convert atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form for other plants. Growing legumes, such as peas and beans, as companion plants can help improve soil fertility by increasing nitrogen levels naturally.
Additionally, companion planting helps create a balanced nutrient cycle by intermixing plants with different nutrient needs and growth patterns. This promotes a healthy soil ecosystem and reduces the risk of nutrient imbalances or deficiencies.
Nitrogen Fixing Plants
Nitrogen-fixing plants play a vital role in companion planting by enhancing soil fertility and supporting the growth of other plants. Some common nitrogen-fixing plants used in companion planting include:
Peas: Peas not only fix nitrogen in the soil but also provide support for other climbing plants.
Beans: Beans are excellent nitrogen fixers and can be interplanted with nitrogen-demanding crops like tomatoes or corn.
Clover: Clover is a ground cover that fixes nitrogen and acts as living mulch, improving soil structure and moisture retention.
By incorporating nitrogen-fixing plants into your garden, you can ensure a continuous and natural supply of this essential nutrient while promoting soil health.
Companion Planting Calendar
Seasonal Planting Guide
The success of companion planting depends on proper timing and understanding of seasonal planting. Different plants have specific growth requirements and thrive under certain temperature and light conditions. By following a seasonal planting guide, you can align your companion planting efforts with optimal growth periods.
When planning your garden, consider factors such as the average last frost date, the length of the growing season, and the specific needs of the plants you are growing. With this information, you can create a comprehensive planting calendar that ensures the proper timing and success of your companion planting endeavors.
Crop Rotation and Companion Planting
Crop rotation is another important aspect of companion planting that helps prevent the buildup of pests and diseases in the soil. By rotating different plant families each year, you decrease the risk of soilborne pests and diseases targeting your crops.
When planning your crop rotation, consider the different nutrient requirements of each plant family and how they can be complemented by other vegetable or cover crop options. Companion planting can be incorporated into crop rotation plans, ensuring a balanced nutrient cycle and minimizing the risk of plant-specific pests and diseases affecting your garden.
Companion Planting Challenges
Managing Plant Competition
While companion planting offers numerous benefits, managing plant competition can sometimes be a challenge. Some plants may compete for resources like water, sunlight, or nutrients, which can lead to stunted growth or reduced yields.
To mitigate plant competition, it is important to consider the growth habits and nutrient requirements of the plants you are pairing. Give plants enough space to grow, provide proper soil amendments and fertilization, and maintain optimal watering and care practices.
Regular monitoring and observation of your garden will help you identify and address any plant competition issues in a timely manner, ensuring the successful growth and productivity of your companion plants.
Avoiding Incompatible Pairings
Not all plant pairings work well together, and some combinations can have negative effects on plant growth and health. It is important to be aware of incompatible pairings that can hinder the success of companion planting.
For example, potatoes and tomatoes, both members of the nightshade family, are prone to similar diseases and pests. Planting them in close proximity can increase the risk of cross-contamination and compromise the health of both crops.
Research and careful planning are essential to avoid incompatible pairings in companion planting. Consult reliable gardening resources, seek advice from experienced gardeners, and keep records of your garden experiments to learn from your own experiences.
Conclusion
Companion planting is an effective gardening technique that maximizes vegetable yield, promotes plant health, and creates a balanced ecosystem. By understanding the relationships between different plant species and strategically pairing them, you can enhance the growth, productivity, and overall health of your garden.
From pest control and soil fertility to flavor enhancement and attracting pollinators, companion planting offers a wide range of benefits for gardeners of all levels. By exploring various methodologies, techniques, and plant pairings, you can create a thriving garden that not only provides a bountiful harvest but also contributes to a sustainable and healthy environment.
So, the next time you plan your vegetable garden, consider the power of companion planting. Embrace the natural synergies and relationships between plants, and watch your garden flourish with abundance and vitality.