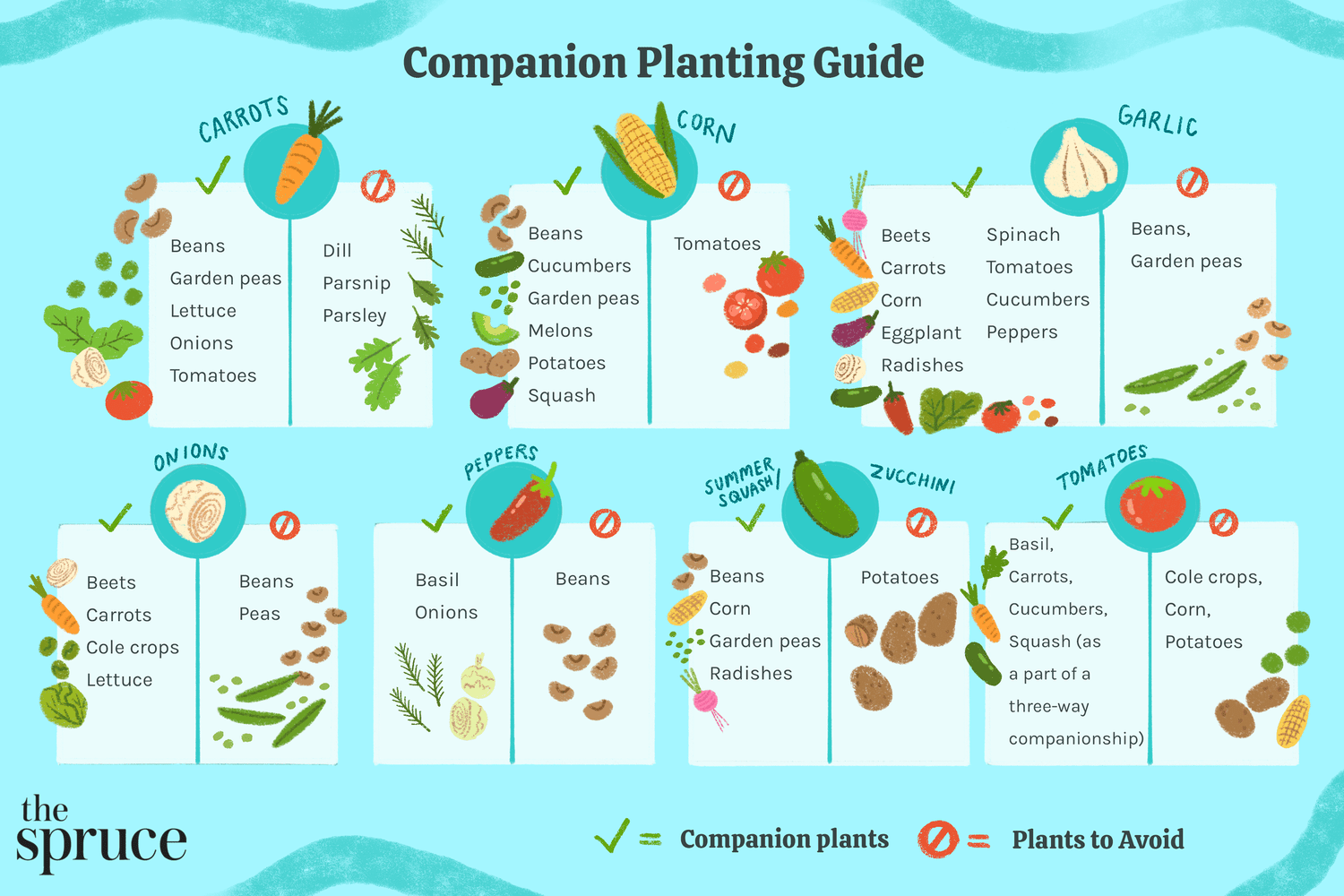
In this article, we’re going to explore the concept of companion planting and how it can maximize the growth potential of your vegetable garden. We’ll discuss the benefits of planting certain vegetables together and which plants should be planted next to each other for optimal results. If you’re interested in off-grid living and have a passion for gardening, this article will provide you with valuable insights to help you create a thriving vegetable garden. So, let’s get started and discover the secrets of companion planting!
Companion Planting: Maximizing Your Vegetable Garden’s Growth Potential
Companion planting is an age-old gardening practice that involves strategically planting different plants together to benefit each other’s growth. By understanding the relationships between plants, you can create a harmonious vegetable garden that maximizes its growth potential. In this article, we will explore the benefits of companion planting, learn about plant relationships, discover complementary plant pairings, and uncover various techniques to attract beneficial insects and repel harmful pests. Additionally, we will discuss herb and vegetable combinations, flower and vegetable combinations, interplanting for space optimization, succession planting strategies, companion planting for soil improvement, crop rotation, common mistakes to avoid, and monitoring and evaluating companion planting. Get ready to unlock the full potential of your vegetable garden!

Benefits of Companion Planting
Companion planting offers a multitude of benefits that can enhance the overall growth and health of your vegetable garden. When plants are properly paired together, they can:
- Provide natural pest control: Certain plant combinations can help deter pests by repelling them or attracting beneficial insects that prey on them. This reduces the need for harmful chemical pesticides.
- Improve pollination: By attracting pollinators such as bees and butterflies, companion plants can aid in the pollination of your vegetable crops, resulting in improved yield and quality.
- Optimize space utilization: Interplanting compatible plants allows you to make the most of your garden space, increasing overall productivity.
- Enhance soil fertility: Some plants have the ability to fix nitrogen in the soil, enriching it for neighboring plants. This can reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers.
- Suppress weeds: Certain plant combinations can naturally suppress weed growth, reducing the need for manual weeding or herbicides.
Understanding Plant Relationships
To successfully implement companion planting, it’s essential to understand plant relationships. Some plants have beneficial effects on each other, while others may be detrimental when planted in close proximity. Here are a few key concepts to keep in mind:
- Mutualism: Mutualistic plant relationships occur when two plants benefit from each other’s presence. For example, beans and corn have a symbiotic relationship, with the beans fixing nitrogen in the soil while the corn provides support for the climbing beans.
- Allelopathy: Some plants release compounds that inhibit the growth of certain other plants. This is known as allelopathy. For instance, juglone, a compound found in walnut tree roots, hinders the growth of many other plants.
- Competition: Certain plants compete for resources such as light, water, and nutrients. Planting two plants with similar resource requirements too close together may result in stunted growth or reduced yields.

Complementary Plant Pairings
Choosing the right plant combinations can be a game-changer in your vegetable garden. Here are some popular companion plant pairings that work synergistically:
- Tomatoes and Basil: Plentifully planting basil near tomatoes can enhance the flavor of the tomatoes, repel pests, and attract pollinators.
- Carrots and Onions: Planting carrots and onions together can help repel pests, as the strong scent of onions masks the smell of carrots, making them less attractive to insects.
- Cabbage and Dill: Dill attracts beneficial insects like ladybugs and hoverflies which prey on cabbage pests like aphids and cabbage worms.
- Marigolds and Beans: Marigolds emit a strong scent that deters bean beetles, while their flowers attract pollinators for improved bean production.
- Roses and Garlic: Planting garlic around roses can help repel aphids and other pests that commonly plague roses.
Attracting Beneficial Insects
Beneficial insects play a crucial role in keeping pesky pests under control and promoting a healthy garden ecosystem. By implementing companion planting techniques, you can attract these beneficial insects and promote natural pest control. Here are some tips:
- Plant flowering herbs: Plants such as lavender, chamomile, and thyme attract beneficial insects like bees, which help pollinate your vegetable crops.
- Integrate native plants: Native plants are often well-adapted to your region and can attract a diverse range of beneficial insects.
- Provide shelter and water sources: Create small habitats within your garden for beneficial insects to take refuge. Simple additions like bee houses, bird baths, or small ponds can make your garden more attractive to beneficial insects.
Repelling Harmful Pests
In addition to attracting beneficial insects, companion planting can also help repel harmful pests. By strategically planting pest-repellent plants, you can create a natural barrier and reduce the need for chemical insecticides. Here are some plant combinations that can keep common garden pests at bay:
- Nasturtiums and Cucumbers: Nasturtiums act as a trap crop, luring aphids away from cucumbers and other susceptible plants. This sacrificial plant diverts pests, protecting your valuable crops.
- Chives and Apples: The strong scent of chives deters apple pests like aphids, making it an ideal companion plant for apple trees.
- Catnip and Squash: Catnip can repel squash bugs and beetles, helping to protect your squash plants from infestations.
- Garlic and Roses: The pungent aroma of garlic deters both aphids and Japanese beetles, offering protection to roses.
Herb and Vegetable Combinations
Companion planting isn’t limited to just vegetables – herbs can also play a vital role in optimizing your garden’s growth potential. Here are some herb and vegetable combinations that work well together:
- Parsley and Tomatoes: Planting parsley near tomatoes can help improve their flavor and repel pests like tomato hornworms.
- Thyme and Cabbage: Thyme can help repel cabbage moths and cabbage worms, protecting your cabbage plants from damage.
- Rosemary and Carrots: Planting rosemary near carrots can deter carrot flies and provide added flavor to your carrots when harvested together.

Flower and Vegetable Combinations
Integrating flowers in your vegetable garden not only adds beauty but also serves various purposes, such as attracting pollinators, deterring pests, and enhancing the overall biodiversity of your garden. Here are some flower and vegetable combinations to consider:
- Sunflowers and Pumpkins: The tall stalks of sunflowers provide a sturdy trellis for climbing pumpkin vines, while the bright flowers attract pollinators.
- Zinnias and Cucumbers: Zinnias attract butterflies and bees, enhancing pollination for your cucumber plants and improving yields.
- Calendula and Broccoli: Calendula flowers attract beneficial insects that prey on pests that commonly attack broccoli, such as aphids and caterpillars.
Interplanting for Space Optimization
When space is limited in your vegetable garden, interplanting becomes a valuable technique to maximize productivity. By carefully selecting compatible plants and staggering their planting times, you can achieve efficient space utilization. Here are some interplanting strategies to consider:
- Radishes and Carrots: Radishes germinate quickly, providing a fast-growing crop while waiting for slower-growing carrots to take off. Plus, radishes can help break up compacted soil, benefiting the carrots’ root development.
- Lettuce and Cabbage: Interplanting lettuce between cabbage plants can provide shade to the soil, helping to retain moisture and reducing weed growth.
- Spinach and Onions: Spinach grows well in the shade provided by onion plants, making them an ideal pairing for small gardens.

Succession Planting Strategies
To ensure a continuous harvest throughout the growing season, succession planting is a valuable technique. By staggering the planting of crops, you can extend your harvest and optimize space utilization. Here are some succession planting strategies:
- Quick-maturing crops: Plant fast-growing crops like lettuce or radishes between slower-growing crops like tomatoes or peppers. Harvest the quick-maturing crops while waiting for the others to reach maturity.
- Continuous sowing: Sow seeds for crops like beans, peas, or corn every two weeks to ensure a continuous harvest over an extended period.
- Crop rotation: Rotate crops each season to prevent the build-up of pests and diseases. This also helps replenish soil nutrients as different plants have varying nutrient needs.
Companion Planting for Soil Improvement
Companion planting can also be used to improve the overall health and fertility of your garden soil. Here are some plant combinations that contribute to soil improvement:
- Legumes and Brassicas: Legumes such as peas and beans have the ability to fix nitrogen from the air and convert it into a usable form for plants. Planting them alongside brassicas like cabbage or broccoli can help replenish nitrogen levels in the soil.
- Alliums and Carrots: Alliums, including onions, garlic, and leeks, have natural pest-repellent properties and can deter carrot flies, which commonly affect carrot crops.
- Deep-rooted plants and shallow-rooted plants: Pairing plants with deep taproots, such as tomatoes or sunflowers, with shallow-rooted plants like lettuce or radishes can help improve soil structure.
Crop Rotation and Intercropping
To maintain soil fertility and prevent the buildup of pests and diseases, crop rotation and intercropping should be incorporated into your gardening practices. Crop rotation involves changing the planting location of crops each year, while intercropping involves planting different crops simultaneously within the same area. These practices help break pest and disease cycles, avoid nutrient deficiencies, and maintain overall soil health.
Companion Planting Tips and Tricks
To make the most of companion planting, here are some additional tips and tricks to keep in mind:
- Plan ahead: Before planting, create a planting design or map to ensure appropriate spacing, companion pairings, and crop rotation.
- Research your crops: Different plants have specific companion preferences and relationship dynamics. Research which plants thrive together and which should be kept apart.
- Experiment and observe: Every garden is unique, so experiment with different plant combinations to find what works best for your specific conditions. Observe and record the results to refine your companion planting strategy over time.
- Keep a balance: While companion planting offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to strike the right balance. Avoid overcrowding plants or relying solely on companion planting as the sole pest control method.
- Stay vigilant: Regularly inspect your garden for any signs of pest infestations or nutrient deficiencies. Prompt action can prevent potential damage to your crops.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Companion Planting
Although companion planting can significantly benefit your vegetable garden, it’s important to avoid common mistakes that may have detrimental effects. Here are a few pitfalls to watch out for:
- Neglecting plant preferences: Ensure you understand each plant’s sun, soil, and watering requirements to create an optimal growing environment.
- Ignoring plant spacing: Overcrowding plants can lead to stunted growth, increased competition, and decreased airflow, making your plants more susceptible to diseases.
- Disregarding crop rotation: Failure to rotate crops can lead to the buildup of pests and diseases in the soil, reducing overall productivity and health of your garden.
- Relying solely on companion planting: While beneficial, companion planting is not a cure-all solution. Implementing other gardening practices like proper watering, fertilization, and pest monitoring is crucial for a successful vegetable garden.
Monitoring and Evaluating Companion Planting
Monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of your companion planting efforts can help you refine your gardening practices and make necessary adjustments. Here are some ways to monitor and evaluate your companion planting:
- Keep a garden journal: Record your planting layout, companion combinations, and observations throughout the growing season. Document any successes, failures, or pest/disease issues.
- Observe plant health and growth: Regularly inspect your plants for signs of nutrient deficiencies, disease, or pest damage. Monitor growth rates and overall health to assess the effectiveness of companion plant pairings.
- Conduct post-harvest evaluations: Evaluate the yield and quality of your crops to determine if your companion planting strategies positively influenced final outcomes.
Conclusion
Companion planting is a valuable practice that can unlock the full potential of your vegetable garden. By understanding plant relationships, implementing complementary plant pairings, attracting beneficial insects, repelling harmful pests, and optimizing space utilization, you can create a thriving garden ecosystem that maximizes growth and productivity. Remember to continuously monitor and evaluate your companion planting efforts, adapt to your garden’s unique conditions, and enjoy the bountiful benefits of companion gardening. Happy planting!