Hi there! In this article, we’ll be discussing the water requirements of raised beds. If you’re into off-grid living or interested in gardening, this topic is perfect for you. We’ll explore whether or not raised beds need more water compared to traditional gardening methods. So, if you’ve ever wondered about the water needs of your raised beds, keep reading to find out the answer and more!
The Water Requirements of Raised Beds
If you’re considering starting a garden or have already dabbled in gardening, you may have come across the concept of raised beds. Raised beds offer many benefits, including increased yield, better drainage, and warmer soil. However, one common question that arises is, “Do raised beds need more water?” In this article, we will explore the water requirements of raised beds and provide you with tips and techniques to efficiently water your plants.
Benefits of Raised Beds
Increased Yield
One of the main advantages of raised beds is the increased yield they can provide. The elevated nature of raised beds allows for better soil aeration and root development, resulting in healthier and more productive plants. With proper watering techniques, raised beds can produce higher yields than traditional ground-level gardening.
Better Drainage
Another benefit of raised beds is improved drainage. The elevated structure of raised beds allows excess water to drain more efficiently, preventing waterlogging and the potential for root rot. This feature is particularly advantageous in areas with heavy rainfall or poor soil drainage.
Warmer Soil
Raised beds absorb and retain heat better than the surrounding ground, which can create a warmer microclimate for your plants. This advantage is particularly useful in regions with cooler climates or during the early spring planting season. Warmer soil temperatures promote faster germination and root growth, ultimately leading to better plant development.
Understanding Water Requirements
Before diving into specific watering techniques, it’s essential to understand the factors that affect water needs in raised beds and the importance of soil type in water retention.
Factors Affecting Water Needs
Several factors can influence the water requirements of your raised beds. These include the type and size of plants, weather conditions, sun exposure, and the stage of plant growth. Larger plants and those in the active growth phase generally require more water than smaller or dormant plants. Likewise, hot and dry weather conditions or prolonged periods of direct sunlight can increase the water needs of your plants.
Importance of Soil Type
Soil composition plays a crucial role in water retention and availability to plants. Different soil types have varying water-holding capacities, with sandy soils draining quickly and clay soils holding onto water for longer periods. Understanding your soil type and making the necessary adjustments can help optimize water retention in raised beds.
Determining Water Needs
To determine the water needs of your raised beds, it’s essential to monitor soil moisture levels regularly. Various techniques can be employed to measure moisture levels effectively.
Watering Techniques for Raised Beds
Efficient watering techniques can ensure that your plants receive the right amount of water without wasting any. Let’s explore some popular watering methods for raised beds.
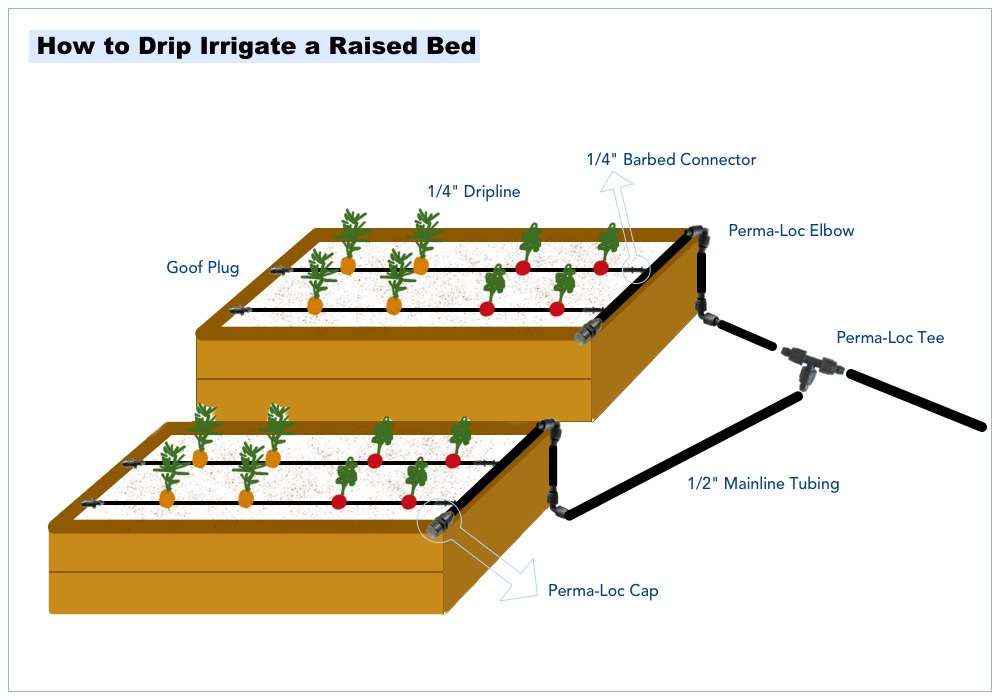
Drip Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation systems are a great option for raised beds as they provide water directly to the base of the plants, minimizing water loss through evaporation and runoff. These systems consist of tubing with small holes or emitters spaced along its length, delivering a slow and consistent water supply to the roots.
Soaker Hoses
Similar to drip irrigation systems, soaker hoses release water directly into the soil at a slow and steady rate. These porous hoses are positioned along the base of your plants, allowing water to seep out slowly and deeply penetrate the soil. Soaker hoses are an affordable and effective option for small to medium-sized raised beds.
Hand Watering
For smaller raised beds or plants requiring more precise watering, hand watering can be a viable option. Using a watering can or hose with a gentle spray nozzle, you can manually water each plant, ensuring they receive the necessary hydration. However, it’s important to water at the base of the plants to minimize water loss through evaporation.
How to Measure Moisture Levels
To ensure your plants are receiving adequate water, you must frequently monitor soil moisture levels. Here are a few methods to help you gauge moisture levels effectively.
Using a Moisture Meter
Moisture meters are handy tools that provide instant readings of soil moisture levels. Simply insert the probe into the soil at various points within your raised beds to obtain accurate readings. These devices are portable, affordable, and a reliable way to assess the watering needs of your plants.
Observing Plant Stress
Plants experiencing water stress often exhibit visible symptoms, such as wilting leaves or yellowing foliage. Observing these signs can help you determine whether your plants require additional hydration. However, it’s important to note that while wilting plants may indicate a need for water, overwatering can also cause similar symptoms.
Testing Soil Moisture by Hand
Another method to measure soil moisture levels is by physically testing the soil with your hand. Insert your finger into the soil up to the first knuckle – if the soil feels moist, it indicates that watering may not be necessary at that moment. However, if the soil feels dry, it’s a clear indication that your plants need water.

Factors Influencing Water Retention
Water retention is crucial for plant health and avoiding water wastage. Several factors can influence the water-holding capacity of your raised bed soil.
Mulching
Mulching is a practice that involves covering the soil surface with a layer of organic materials such as straw, wood chips, or leaves. This layer acts as a protective barrier, reducing evaporation and regulating soil moisture levels. Mulching can significantly improve water retention in raised beds and also helps suppress weed growth.
Companion Planting
Companion planting involves strategically planting certain plants together to achieve various benefits, including improved water retention. Some companion plants have deep root systems that can break up compacted soil, allowing water to penetrate deeper into the ground. Additionally, companion plants can provide shade to other plants, reducing evaporation and water loss.
Proper Soil Preparation
Proper soil preparation is essential for optimizing water retention in raised beds. Adding organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, can enhance the soil’s ability to hold moisture while improving its structure. Loosening the soil before planting also allows water to penetrate deeper, preventing runoff and promoting better root growth.
Mulching Methods for Moisture Retention
Mulching is an effective technique for conserving soil moisture in raised beds. Let’s explore some popular organic mulch types and the correct method of applying and maintaining mulch coverage.
Organic Mulch Types
Organic mulches, such as straw, wood chips, leaves, and compost, provide numerous benefits for raised beds. They not only help retain soil moisture but also improve soil fertility as they break down over time. When selecting organic mulch, consider the availability and suitability of the material for your particular plants and gardening needs.
Applying Mulch Correctly
To apply mulch correctly, spread a layer of organic material approximately 2-4 inches thick on the soil surface around your plants. Avoid placing mulch directly against plant stems to prevent excess moisture retention, which can lead to rot. Leaving a small gap between the mulch and plant stems allows for proper airflow and discourages the growth of harmful pathogens.
Maintaining Mulch Coverage
As organic mulch material decomposes over time, it will need replenishing to maintain adequate coverage. Inspect the mulch periodically, and if it appears thin or has started breaking down, add a fresh layer to ensure optimal moisture retention and weed suppression.

Companion Planting for Water Conservation
Companion planting not only benefits individual plants but also promotes efficient water usage in your raised beds. Let’s explore some of the advantages companion planting offers for water conservation.
Beneficial Plant Combinations
Certain plant combinations have a mutually beneficial relationship when grown together. For example, planting water-loving crops alongside plants with deep taproots can help draw moisture deeper into the soil, making it available to a wider range of plants. Research and experiment with different companion planting combinations to find the best options for your raised bed.
Natural Pest Control
Companion planting can also help naturally control pests, reducing the need for chemical interventions that can harm water quality. Some companion plants, when grown alongside vulnerable plants, emit natural substances that deter pests. This symbiotic relationship not only protects your plants but also helps conserve water by avoiding the need for excess watering due to pest damage.
Watering Requirements for Companion Plants
When practicing companion planting, it’s important to consider the watering requirements of each plant. Some companion plants may have differing water needs, so it’s essential to strike a balance to ensure all plants receive adequate hydration. Grouping plants with similar water requirements together can make watering easier and more efficient.
Soil Preparation Techniques for Improved Water Retention
Proper soil preparation is key for water retention in raised beds. Here are some techniques to help improve your soil’s ability to hold moisture effectively.
Amending Soil with Organic Matter
Incorporating organic matter into your soil is a beneficial practice for various reasons, including improved water retention. Adding compost, well-rotted manure, or other organic materials to your raised beds increases the soil’s ability to hold onto moisture, reducing the frequency of watering needed.
Loosening Soil Structure
Before planting in your raised beds, ensure the soil is well loosened to promote deep root growth and water penetration. Loosening the soil structure also helps prevent compaction, allowing water to flow freely and not collect on the surface or cause runoff. Use a garden fork or tiller to loosen the soil, breaking up any clumps and ensuring it is sufficiently aerated.
Improving Soil Fertility
Optimum soil fertility is necessary for healthy plant growth. Well-nourished plants are better equipped to withstand dry periods and resist water stress. Prior to planting, it’s important to enrich your soil with organic matter and appropriate fertilizers to ensure your plants have the necessary nutrients to thrive and efficiently use available water resources.

Signs of Water Stress in Raised Beds
To maintain healthy plants, it’s crucial to identify signs of water stress early on. Here are some common indicators to watch out for in your raised beds.
Wilting Plants
Wilting leaves and stems are often a clear sign of water stress. When a plant does not receive enough water, it causes a loss of turgor pressure, resulting in wilting. However, it’s important to note that overwatering can also lead to wilting, so it’s essential to assess other factors before adjusting your watering regimen.
Yellowing Leaves
Yellowing leaves, particularly on new growth, can indicate water stress. When plants lack adequate water, they prioritize supplying water to essential areas, such as the roots, and may divert resources away from less vital parts, such as leaves. This diversion of resources can cause yellowing or browning of foliage.
Stunted Growth
If your plants aren’t growing as expected or seem to be lagging in development, it could be a sign of water stress. Insufficient water hampers the plant’s ability to take up nutrients from the soil, affecting their growth rate and overall size.
Water-Saving Tips for Raised Beds
Conserving water in raised beds not only benefits the environment but also saves you time and effort. Here are some water-saving tips to help you make the most of this precious resource.
Proper Timing of Watering
Watering your raised beds at the right time of day can greatly impact water retention. Watering early in the morning or late in the evening helps reduce evaporation and allows plants to absorb moisture before the heat of the day. Avoid watering during the hottest part of the day, as the water will likely evaporate before reaching the plant’s roots.
Watering at the Base of Plants
When watering your raised beds, aim to deliver water directly to the base of the plants. Watering the leaves or surrounding soil can lead to unnecessary evaporation and water loss. Focusing your watering efforts at the base of the plants ensures that water reaches the roots where it’s needed most.
Avoiding Overwatering
While it’s crucial to provide plants with adequate water, overwatering can be just as detrimental as underwatering. Overwatering can lead to waterlogged soil conditions, which can suffocate the roots and promote fungal diseases. It’s essential to strike a balance and give plants enough water to thrive without drowning them.
Importance of Regular Inspections
Regularly inspecting your raised beds is crucial for identifying potential problems early on. By conducting routine inspections, you can address issues promptly and prevent them from escalating. Let’s explore some key aspects to consider during your inspections.
Checking for Pest Infestations
Pests can wreak havoc on your plants and water resources. Inspecting your raised beds for signs of pest infestations, such as chewed leaves or insect activity, allows you to take immediate action, minimizing potential damage and reducing the need for excessive watering due to pest-related stress.
Identifying Disease Symptoms
Diseases can impact plant health and reduce their ability to take up water efficiently. Regularly inspecting your raised beds for disease symptoms, such as discolored spots or unusual growth patterns, can help you identify problems early on. Treating diseases promptly can prevent further damage, conserving your water resources and ensuring the health of your plants.
Assessing Soil Moisture Levels
During your inspections, it’s important to assess soil moisture levels to determine if your watering regimen is sufficient. By regularly monitoring soil moisture, you can make adjustments as needed, keeping your plants adequately watered without wasting water through overwatering or underwatering.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
In ensuring proper water requirements for raised beds, it’s important to be aware of common mistakes that can hinder plant health and water conservation efforts. Let’s discuss some common pitfalls to avoid.
Underwatering
Underwatering your raised beds will leave your plants thirsty and may result in stunted growth or even plant death. It’s important to establish a consistent watering routine and monitor soil moisture levels regularly to ensure your plants are receiving enough water.
Overwatering
On the other hand, overwatering can lead to numerous problems. Excessively wet soil can suffocate the roots, promote the growth of root rot pathogens, and reduce the uptake of nutrients. Always evaluate soil moisture levels before watering and consider the specific water requirements of your plants to avoid overwatering.
Inadequate Drainage
Raised beds are designed to provide better drainage than traditional ground-level gardens. However, inadequate drainage can still become an issue. Ensure that your raised beds have proper drainage systems in place and avoid planting in areas with poor natural drainage, as this can lead to waterlogging and root rot.
Using Technology for Efficient Watering
In today’s technologically advanced world, there are various tools and devices available to assist with efficient watering in raised beds. Let’s explore some technological options that can help you conserve water and optimize plant health.
Smart Irrigation Systems
Smart irrigation systems utilize sensors and timers to deliver water based on plant needs and environmental conditions. These systems can be programmed to water at specific times, adjust watering based on soil moisture levels, and even connect to weather forecasts to make real-time watering adjustments. Smart irrigation systems are a convenient and efficient way to ensure your raised beds receive the optimal amount of water.
Weather-Based Watering Controls
Weather-based watering controls use local weather data to adjust watering schedules and amounts accordingly. By incorporating real-time weather information, these controls can adapt to changing conditions, ensuring that your plants receive the appropriate amount of water based on external factors such as rainfall and evaporation rates.
Automated Soil Moisture Sensors
Soil moisture sensors are devices that measure the moisture content of the soil and provide data to help determine watering needs. These sensors can be installed in raised beds to provide real-time information about soil moisture levels. By utilizing automated soil moisture sensors, you can avoid guesswork and ensure that your plants are watered when needed, saving both water and time.
Conclusion
Raised beds offer many benefits for gardeners, including increased yield, better drainage, and warmer soil. Understanding the water requirements of raised beds is essential for efficiently growing healthy plants while conserving water. By considering factors such as soil type, implementing proper watering techniques, and utilizing technology, you can ensure your raised beds receive the optimal amount of water, resulting in vibrant and thriving plants. Remember to regularly inspect your raised beds, avoid common watering mistakes, and make adjustments as needed. With proper care and attention, your raised beds will not only flourish but also contribute to a sustainable and eco-friendly gardening practice.




