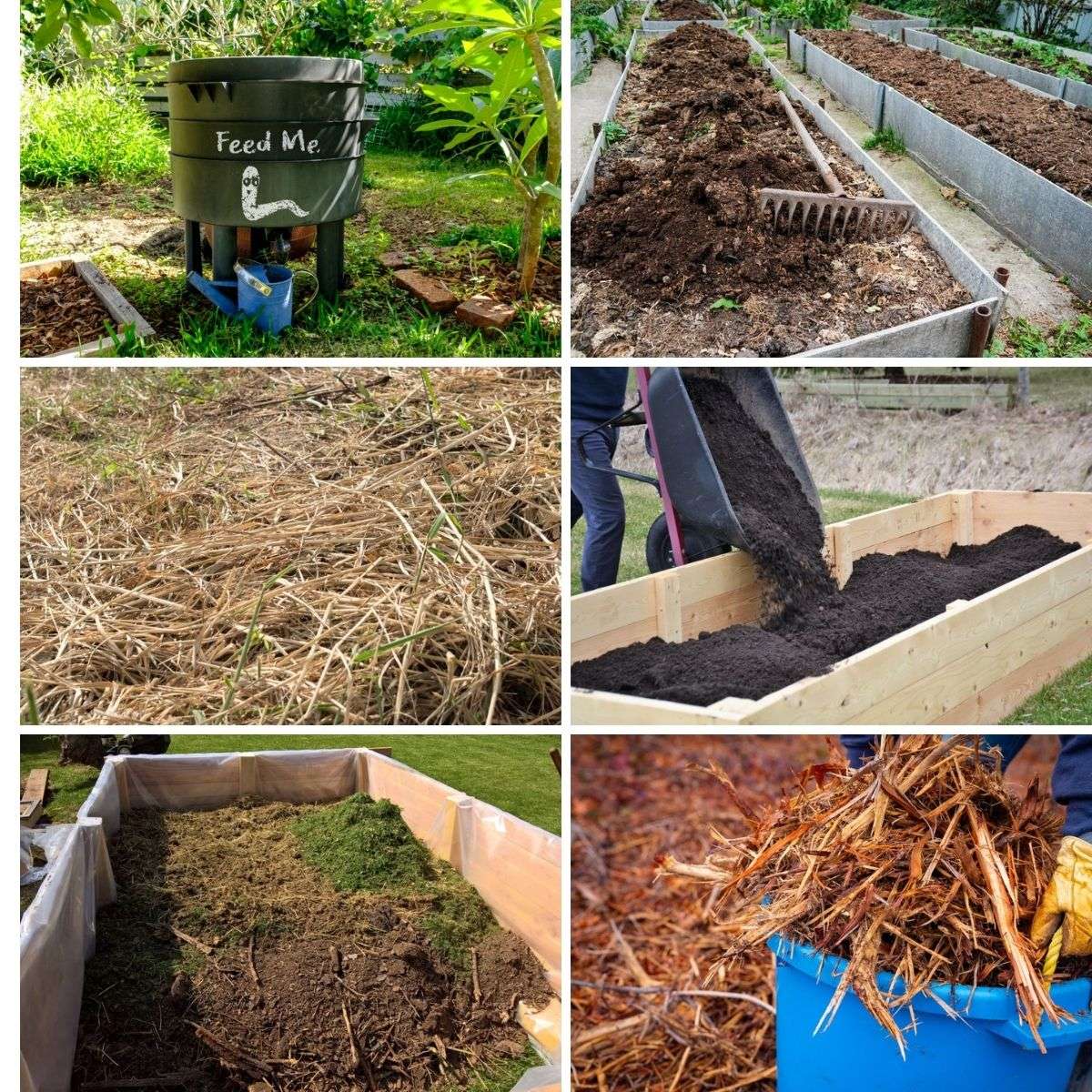
Are you thinking of starting a garden but worried about the challenges of filling raised garden beds with compost, mulch, and soil? Building a smaller raised garden bed could be a cost-effective solution, as it requires less material. Utilizing local resources, such as deadwood, soil from nearby forests, and grass clippings, can also be a cheaper way to fill your garden beds. However, it’s important to consider the specific needs of your plants when selecting compost, soil, and mulch. Raised garden beds offer several benefits, including overcoming poor nutrient soil, pest issues, and providing easier gardening, especially for older individuals. To fill your raised garden bed, you have various options to choose from, including local soil, forest soil, logs, grass clippings, compost, worm castings, animal manure, mulch, soil mix, peat moss, and cover crops. Keep in mind that smaller raised garden beds are easier to fill and manage, making the process simpler and more enjoyable.
Challenges of Filling Raised Garden Beds with Compost, Mulch, and Soil
Filling raised garden beds can be a challenge due to the need for appropriate compost, mulch, and soil. These materials are essential for providing the necessary nutrients, moisture retention, and drainage for plants to thrive in a raised bed. However, finding the right balance of materials and ensuring cost-effectiveness can be a daunting task. In this article, we will explore various methods and materials for filling raised garden beds and discuss the challenges and considerations associated with each option.
Cost-Effectiveness of Smaller Raised Garden Beds
When it comes to filling raised garden beds, the size of the bed can greatly impact the cost-effectiveness of the materials needed. Building a smaller raised garden bed can be more cost-effective compared to larger ones. This is because smaller beds require less filling material, such as compost and soil. By reducing the material requirement, you can save money while still enjoying the benefits of a raised bed.
In addition to reduced material requirements, smaller raised garden beds also allow for better quality control. With a smaller bed, you can focus on using high-quality compost and mulch that are tailored to meet the specific needs of your plants. This way, you can ensure that your plants receive the optimal nutrients and growing conditions without overspending on excessive amounts of filling materials.
The potential savings from choosing smaller raised garden beds can be significant, especially for gardeners on a budget. With proper planning and consideration, you can create a cost-effective and productive raised bed garden that suits your needs and preferences.
Utilizing Local Materials to Fill Raised Garden Beds
Another way to reduce the cost of filling raised garden beds is by utilizing local materials that are readily available in your area. Local materials not only offer cost savings but can also be more environmentally friendly by reducing transportation costs and supporting local sustainability efforts. Here are a few examples of local materials that can be used to fill raised garden beds:
Using Deadwood
If you live in an area with forests or woodlands nearby, one cost-effective option is to gather deadwood and use it as a filling material. Deadwood, or fallen branches, can be broken down into smaller pieces and added to the raised bed to improve drainage and aeration. Over time, the deadwood will decompose and release nutrients into the soil, benefiting your plants.
Incorporating Soil from Nearby Forests
Another local material that can be used to fill raised garden beds is soil from nearby forests. Forest soil is typically rich in organic matter and nutrients, making it an excellent choice for filling raised beds. To collect forest soil, ensure that you have permission from the landowner or relevant authorities. This way, you can gather soil responsibly and sustainably without causing any harm to the surrounding environment.
Recycling Grass Clippings
If you have a lawn or access to grassy areas, recycling grass clippings can be a cheap and sustainable way to fill raised garden beds. Grass clippings can be used as a top layer or mixed with other filling materials to improve moisture retention and organic matter content in the soil. Be sure to avoid using grass clippings treated with herbicides or pesticides to prevent any potential harm to your plants.
By utilizing local materials such as deadwood, forest soil, and grass clippings, you can significantly reduce the cost of filling raised garden beds while still providing the necessary nutrients and growing conditions for your plants.
Considering the Specific Needs of Plants
When filling raised garden beds, it is crucial to consider the specific needs of the plants you will be growing. Different plants have varying requirements in terms of soil composition, pH levels, nutrient availability, and moisture needs. By understanding these needs, you can choose the most suitable compost, soil, and mulch to create an optimal growing environment in your raised bed. Here are a few factors to consider:
Understanding Soil Composition
Some plants thrive in well-draining soil, while others prefer a more moisture-retaining environment. Understanding the composition of your soil and the specific needs of your plants will help you select the appropriate filling materials. For example, if you have heavy clay soil, adding organic matter such as compost and mulch can improve its structure and drainage.
Analyzing pH Requirements
Different plants have different pH preferences. Some prefer acidic soil, while others thrive in alkaline conditions. Testing your soil’s pH and adjusting it accordingly can ensure that your plants receive the ideal pH levels for optimal growth. Adding lime or sulfur can help balance the pH levels in your raised bed.
Identifying Nutrient Requirements
Plants require essential nutrients for healthy growth. Understanding the specific nutrient requirements of your plants, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, will help you select the right compost and fertilizers to provide the necessary nutrients. Incorporating nutrient-rich materials like compost, worm castings, or animal manure can help meet these requirements.
Determining Moisture Needs
Different plants have varying moisture needs. Some prefer moist soil, while others tolerate drier conditions. Consider the moisture retention capabilities of your chosen filling materials to ensure that your plants receive the appropriate moisture levels. For example, incorporating mulch or peat moss can help retain moisture in the soil, benefiting moisture-loving plants.
By considering the specific needs of your plants, you can choose the most suitable filling materials for your raised garden beds and create an optimal growing environment that promotes healthy growth and abundant harvests.

Benefits of Raised Garden Beds
Before delving into the methods and materials for filling raised garden beds, it is essential to understand the benefits of utilizing raised beds in the first place. Raised garden beds offer several advantages for both novice and experienced gardeners. Here are some key benefits:
Improving Nutrient Availability
One of the significant benefits of raised garden beds is the ability to control and optimize nutrient availability. By filling the beds with nutrient-rich compost, soil, and other organic materials, you can provide a fertile environment where plants can access essential nutrients easily. This leads to healthier plant growth, better yield, and improved nutritional quality of the harvest.
Minimizing Pest Issues
Raised garden beds can help minimize pest issues by creating barriers between your plants and potential threats, such as invasive weeds and ground-dwelling pests. The elevated design of raised beds makes it more difficult for weeds to invade your garden, reducing competition for resources. Additionally, the controlled environment of raised beds can deter pests such as slugs, snails, and certain types of crawling insects.
Reducing Gardening Efforts
The raised height of garden beds can provide ergonomic benefits by reducing strain on your back and knees. Tending to plants and performing various gardening tasks, such as weeding, planting, and harvesting, becomes more comfortable and enjoyable. This is especially beneficial for older individuals or those with physical limitations, as raised beds offer improved accessibility and ease of maintenance.
Catering to the Needs of Older Individuals
Raised garden beds are particularly advantageous for older individuals who may face challenges associated with stooping, kneeling, and bending. The elevated design of raised beds eliminates the need for excessive bending or kneeling, allowing older gardeners to continue pursuing their gardening passion without unnecessary strain on their bodies. This promotes gardening as a form of physical activity and therapeutic hobby for individuals of all ages.
By understanding the benefits of raised garden beds, you can appreciate the advantages they offer and make informed decisions when selecting the right materials to fill your raised beds.
Methods and Materials for Filling Raised Garden Beds
Choosing the right methods and materials for filling raised garden beds is crucial to creating a successful growing environment. There are various options available, each with its own advantages and considerations. Let’s explore some commonly used methods and materials for filling raised beds:
Using Local Soil
Using locally sourced soil is a convenient and cost-effective way to fill raised garden beds. Before using local soil, it is essential to evaluate its quality. Look for soil that is free from contaminants, such as heavy metals or pesticide residues. Amending the soil with organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, can improve its nutritional content and structure.
Utilizing Forest Soil
Forest soil, as mentioned earlier, is a nutrient-rich option for filling raised garden beds. Accessing nearby forests and collecting soil can be a rewarding way to incorporate local materials into your garden. However, it is important to gather soil responsibly and sustainably, ensuring minimal disruption to the forest ecosystem. Preparing the soil by removing large debris and ensuring it is free from contaminants is also crucial.
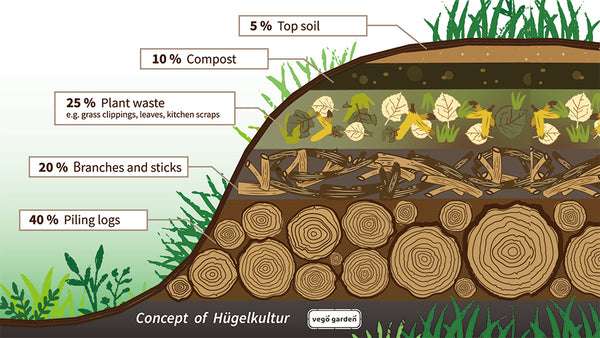
Incorporating Logs
Using logs as a base layer in raised garden beds can provide several benefits. Logs enhance drainage and aeration, preventing waterlogging and promoting healthy root development. Additionally, logs decompose slowly over time, releasing valuable nutrients into the soil. Opt for untreated logs, preferably from hardwood trees, to avoid introducing harmful chemicals into the soil.
Grass Clippings as Filling Material
Grass clippings can serve as a valuable filling material for raised garden beds. They contribute organic matter, which improves soil structure and moisture retention. Layering grass clippings with other filling materials, such as compost or soil mix, helps create a balanced nutrient-rich environment for your plants. Ensure that the grass clippings are untreated and free from herbicides or pesticides.
The Importance of Compost
Compost is a fundamental component when filling raised garden beds. It adds organic matter, improves soil structure, and provides a steady supply of nutrients for plants. Opt for high-quality compost that has gone through proper decomposition to ensure it is free from pathogens and weed seeds. Homemade compost or locally sourced compost can be economical and sustainable options.
Utilizing Worm Castings
Worm castings, also known as vermicompost, are rich in nutrients and beneficial microorganisms. Incorporating worm castings into raised garden beds enhances soil fertility and promotes vigorous plant growth. You can either purchase worm castings or set up a vermicomposting system at home to produce your own. Worm castings are particularly beneficial for plants that require a nutrient-rich growing medium.
The Role of Animal Manure
Animal manure, when used appropriately, can be an excellent source of nutrients for raised garden beds. Organic, well-rotted manure from herbivorous animals, such as cows or horses, is preferable. Avoid using fresh manure or manure from carnivorous animals to prevent the introduction of harmful bacteria or pathogens. Mix the manure into the filling materials to enrich the soil and provide essential nutrients.
Using Mulch for Raised Garden Bed Filling
Mulch is a versatile material that can serve multiple purposes when filling raised garden beds. It helps conserve moisture, suppress weed growth, regulate soil temperature, and enhance soil fertility as it breaks down over time. Organic mulches, such as straw, wood chips, or leaves, are preferable as they add organic matter to the soil as they decompose.
Choosing the Right Soil Mix
Creating a suitable soil mix for raised garden beds is essential for promoting healthy plant growth. The ideal soil mix should have a balanced texture, good drainage, and sufficient organic matter. A common soil mix for raised beds consists of a combination of topsoil, compost, and another amendment such as perlite or vermiculite to improve drainage and aeration.
Incorporating Peat Moss
Peat moss is a valuable amendment for improving soil structure and moisture-holding capacity in raised garden beds. It adds organic matter, increases water retention, and enhances nutrient availability. However, it is essential to use peat moss responsibly, as its extraction can have negative environmental impacts. Consider using alternatives such as coconut coir as a more sustainable option.
Utilizing Cover Crops
Cover crops, also known as green manure, can be grown and incorporated into raised garden beds to enrich the soil with organic matter. Cover crops, such as legumes or grasses, fix nitrogen from the air, add organic material to the soil, and improve soil structure. Before planting cover crops, consider the specific needs of your main crops and choose cover crops that complement them.
By utilizing a combination of these methods and materials, you can create a healthy and productive growing environment in your raised garden beds, while taking into account factors such as cost-effectiveness, nutrient requirements, and environmental sustainability.

Using Local Soil
If you have access to local soil, it can be a convenient and cost-effective option for filling raised garden beds. Local soil can be sourced from your property or nearby areas, reducing the need for purchasing large amounts of filling material. Before using local soil, it is important to evaluate its quality to ensure it is suitable for your plants. Here are a few considerations when using local soil:
Evaluating Soil Quality
Evaluate the quality of the local soil by assessing its texture, drainage, and nutrient content. Sandy soil tends to drain quickly, while clay soil retains moisture. Optimal soil for raised garden beds should have a balanced texture that allows for good drainage while retaining adequate moisture. Additionally, test the soil’s nutrient content to determine if any amendments are necessary.
Amending Soil for Improved Nutrition
If the local soil lacks essential nutrients, it may need amendments to improve its fertility. Adding organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, can enhance the nutrient content and structure of the soil. Incorporating organic matter improves soil moisture retention and provides a steady supply of nutrients for your plants.
Testing for Contaminants
Before using local soil, it is crucial to test for any contaminants that may be present. Soil contamination can come from various sources, including heavy metals, pesticide residues, or pollutants from nearby industrial activities. Testing for contaminants ensures the safety of your plants and prevents any potential harm to the environment or human health.
Testing local soil can be done through commercial soil testing services or by using home testing kits. Make sure to follow proper sampling protocols and consult with local agricultural extension offices or experts for guidance on interpreting the test results and determining appropriate actions.
By properly evaluating the quality of local soil and making necessary amendments, you can confidently utilize this resource to fill your raised garden beds, resulting in healthier plants and a more sustainable gardening practice.
Utilizing Forest Soil
If you have access to nearby forests, utilizing forest soil can be a great option for filling raised garden beds. Forest soil is typically rich in organic matter, minerals, and beneficial microorganisms, making it an excellent medium for plant growth. Here are some considerations when utilizing forest soil:
Accessing Nearby Forests
Accessing nearby forests for soil collection may require permission from the landowner or relevant authorities. Before collecting forest soil, ensure that you are aware of any regulations or restrictions that may apply. Be respectful of the natural environment and practice sustainable soil collection methods to minimize any negative impacts.
Collecting and Preparing Forest Soil
When collecting forest soil, focus on the topmost layer, known as the forest floor. This layer contains decomposed organic matter, leaf litter, and minerals that contribute to the soil’s fertility. Use a spade or shovel to gather the soil, making sure to remove any large debris or rocks. It is important not to disturb the underlying soil layers or dig too deep, as it may disrupt the ecosystem.
Once collected, the forest soil should be prepared for use in raised garden beds. Remove any non-organic debris and break up clumps to ensure a uniform consistency. Despite its natural fertility, forest soil may still require amendments depending on the specific needs of your plants. Consider testing the soil’s nutrient levels and pH to determine if any adjustments are necessary.
Benefits of Forest Soil
Forest soil offers numerous benefits for raised garden beds. Its high organic matter content improves soil structure and water-holding capacity, promoting healthy root development and reducing the risk of waterlogging. The presence of beneficial microorganisms in forest soil enhances nutrient availability and plant health. Additionally, forest soil can provide a natural source of minerals that are beneficial for plant growth. By utilizing forest soil, you can create a fertile and productive growing environment in your raised garden beds.

Incorporating Logs
Incorporating logs as a filling material in raised garden beds can offer multiple benefits for plant growth and soil health. Logs not only provide organic matter as they break down but also enhance drainage and aeration in the raised bed. Here are some advantages and considerations when using logs:
Creating a Sustainable Garden Bed Base
Using logs as a base layer in raised garden beds is a sustainable practice that utilizes natural resources efficiently. When logs decompose, they release nutrients into the soil, contributing to the long-term fertility of the bed. This method reduces the need for additional filling materials and provides a foundation for healthy plant growth.
Enhancing Drainage and Aeration
Logs have natural channels and pores that promote good drainage and aeration in raised garden beds. As water flows through the logs, excess moisture can be efficiently drained away, preventing waterlogging that can lead to root rot and other plant diseases. The air pockets created by the decomposing wood also improve oxygen circulation in the soil, creating an optimal environment for root development.
Decomposition and Nutrient Release
Logs decompose slowly over time, gradually releasing valuable nutrients into the soil. As the logs break down, they provide a continuous supply of organic matter, promoting the growth of beneficial microorganisms that contribute to soil health. The decomposing logs also attract earthworms and other soil-dwelling organisms, further enriching the soil and improving its structure.
When incorporating logs into raised garden beds, it is essential to consider their size and placement. Opt for logs from hardwood trees, as they decompose more slowly compared to softwoods. Place the logs at the bottom of the bed, ensuring they do not touch the sides to prevent any potential issues with moisture retention or rot.
By incorporating logs into the filling materials of raised garden beds, you can create a sustainable growing environment that benefits plant growth, soil health, and long-term fertility.
Advantages of Smaller Raised Garden Beds
When it comes to raised garden beds, the size of the bed plays a significant role in both cost-effectiveness and manageability. Smaller raised garden beds offer several advantages compared to larger ones. Here are some benefits of opting for smaller raised garden beds:
Reduced Filling Requirements
One of the main advantages of smaller raised garden beds is the reduced amount of filling material required. Smaller beds have a smaller surface area to fill, which means less compost, soil, and mulch are needed. This reduces the initial cost of filling the beds, making it more affordable, particularly for those on a tight budget.
Ease of Management
Smaller raised garden beds are much easier to manage and maintain compared to larger ones. With a smaller bed, it is easier to reach into the center without having to step or reach across long distances. Tasks such as planting, weeding, and harvesting are more convenient and less strenuous on the body. This is especially beneficial for older individuals or those with physical limitations who may have difficulty maneuvering around larger beds.
Improved Accessibility
Smaller raised garden beds offer improved accessibility and ease of use, making gardening more enjoyable for individuals of all ages and abilities. The reduced height of the bed makes it easier to access and tend to plants without the need for excessive bending or kneeling. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with mobility issues or those who use mobility aids.
By opting for smaller raised garden beds, you can create a more cost-effective, manageable, and accessible gardening experience while still enjoying all the benefits that raised beds have to offer.
In conclusion, filling raised garden beds with compost, mulch, and soil can present several challenges. However, with careful consideration, it is possible to overcome these challenges and create a productive and sustainable growing environment. Whether you choose to build smaller raised garden beds, utilize local materials, or consider the specific needs of your plants, the key is to strike a balance between cost-effectiveness, environmental sustainability, and optimal plant growth. By incorporating the right methods and materials into your raised garden beds, you can enjoy the benefits of improved nutrient availability, pest control, and reduced gardening efforts. So get ready to roll up your sleeves, fill those beds, and start reaping the rewards of your raised garden. Happy gardening!





